The Present Tense Chart with Examples is the heartbeat of the English language. Whether you’re chatting with a friend, writing an email, or giving a presentation, you’re using the present tense more often than you realize. It’s the tense we rely on to describe daily habits, ongoing actions, facts, and experiences that connect the past to the present.
But here’s the thing: most articles gloss over important rules, mix up structures, or skip examples that actually help you understand how to use the tense in real life. In this guide, we’ll go beyond the basics. You’ll not only learn what the present tense is, but you’ll see detailed breakdowns, easy-to-follow charts, and examples that make sense in everyday English.
What Is the Present Tense?
The present tense refers to actions or situations happening right now, actions that happen regularly, or facts that are always true.
Definitions from Leading Sources:
-
Oxford Dictionary: The present tense is “the verb form that shows the action is happening now.”
-
Cambridge Dictionary: It’s “a verb form used to describe actions that are happening or are generally true.”
We use the present tense when:
◉ Something is happening now
◉ We talk about routines or habits
◉ We’re stating general truths
◉ We connect the past to the present in a meaningful way
Why Understanding the Present Tense Matters
Learning how to use the present tense accurately helps you:
◉ Communicate more clearly
◉ Sound fluent and natural in conversation
◉ Avoid common grammar mistakes
◉ Strengthen your writing and speaking
It’s the foundation of English grammar. Get this right, and you’ll feel more confident expressing yourself every day.
The Four Present Tense Forms (And What Makes Each One Unique)
Many learners only remember the names, but few understand the difference between them. Let’s fix that.
Simple Present Tense
Definition: Describes habits, routines, general truths, and scheduled events.
Structure:Subject + base verb (+s/es for third person singular)
Examples:
-
I drink coffee every morning.
-
She walks to school.
-
The sun rises in the east.
When to use:
- Daily activities
Universal truths
◉ Scheduled timetables (e.g., The train arrives at 6 p.m.)
Present Continuous Tense
Definition: Describes actions that are happening right now or are in progress.
Structure:Subject + am/is/are + verb-ing
Examples:
-
I am reading a book.
-
They are working on a project.
-
Is she watching TV?
When to use:
◉ Actions happening at the moment
◉ Temporary events
◉ Changes or trends (e.g., It’s getting colder)
Present Perfect Tense
Definition: Connects past actions or events to the present moment.
Structure:Subject + have/has + past participle
Examples:
-
I have visited London twice.
-
She has lost her keys.
-
Have you eaten dinner?
When to use:
◉ Experiences up to now
◉ Completed actions with present relevance
◉ Recently finished tasks (e.g., He has just left)
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Definition: Describes actions that started in the past and are still continuing now.
Structure:Subject + have/has + been + verb-ing
Examples:
-
We have been studying for three hours.
-
She has been waiting since morning.
-
Have they been working all day?
When to use:
◉ Ongoing actions that started in the past
◉ To show duration
◉ To highlight the result of continuous action
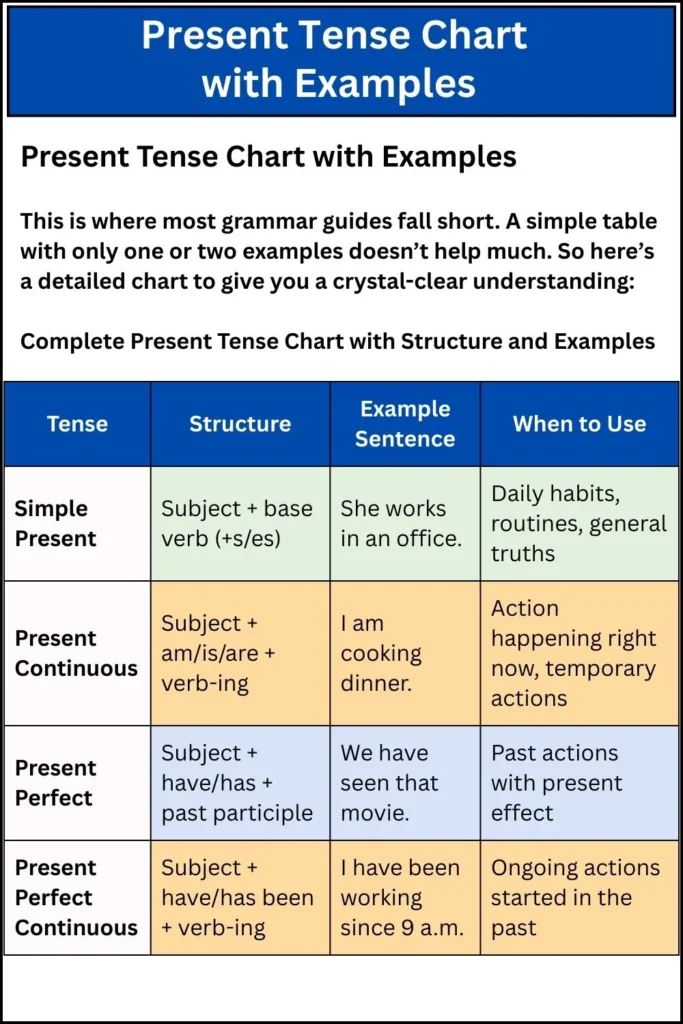
Present Tense Chart with Examples
This is where most grammar guides fall short. A simple table with only one or two examples doesn’t help much. So here’s a detailed chart to give you a crystal-clear understanding:
Complete Present Tense Chart with Structure and Examples
| Tense | Structure | Example Sentence | When to Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Present | Subject + base verb (+s/es) | She works in an office. | Daily habits, routines, general truths |
| They play football on Sundays. | |||
| Present Continuous | Subject + am/is/are + verb-ing | I am cooking dinner. | Action happening right now, temporary actions |
| Are they playing outside? | |||
| Present Perfect | Subject + have/has + past participle | We have seen that movie. | Past actions with present effect |
| He has completed his homework. | |||
| Present Perfect Continuous | Subject + have/has been + verb-ing | I have been working since 9 a.m. | Ongoing actions started in the past |
Common Mistakes with Present Tense (And How to Avoid Them)
Many learners make the same avoidable mistakes. Let’s clear up a few:
◉ Wrong subject-verb agreement:
Wrong: She go to school.
Right: She goes to school.
◉ Confusing simple and continuous tenses:
Wrong: I am know the answer.
Right: I know the answer.
(“Know” is a stative verb, usually not used in continuous form)
◉ Using past tense where present perfect fits better:
Wrong: I saw that movie.
Right: I have seen that movie.
(When the exact time isn’t important or it connects to now)
How to Form Each Present Tense – With Detailed Rules and Variations
Let’s now break down each tense with its rules, subject-verb agreement, and specific cases that often confuse learners.
Simple Present Tense – Formation Rules
Affirmative Structure:Subject + base form (+s/es for he/she/it)
Negative Structure:Subject + do/does not + base form
Question Structure:Do/Does + subject + base form
Verb Form Rules:
◉ Add -s for third-person singular (e.g., He runs.)
◉ Add -es if the verb ends in -ch, -sh, -ss, -x, -o (e.g., She watches TV.)
◉ Drop -y and add -ies if the verb ends in consonant + y (e.g., He flies a drone.)
◉ Do not add s/es for I/you/we/they
Present Continuous Tense – Formation Rules
Affirmative Structure:Subject + am/is/are + verb-ing
Negative Structure:Subject + am/is/are + not + verb-ing
Question Structure:Am/Is/Are + subject + verb-ing?
Verb-ing Rules:
◉ For most verbs, just add -ing
◉ Drop -e and add -ing (e.g., make → making)
◉ Double the last letter if verb ends in consonant + vowel + consonant (e.g., run → running)
Present Perfect Tense – Formation Rules
Affirmative Structure:Subject + have/has + past participle
Negative Structure:Subject + have/has + not + past participle
Question Structure:Have/Has + subject + past participle?
Usage Tips:
◉ Use “have” for I, you, we, they
◉ Use “has” for he, she, it
◉ Past participles are often irregular (e.g., go → gone, eat → eaten)
Present Perfect Continuous Tense – Formation Rules
Affirmative Structure:Subject + have/has + been + verb-ing
Negative Structure:Subject + have/has + not + been + verb-ing
Question Structure:Have/Has + subject + been + verb-ing?
Time Expressions to Use:
◉ Use “for” for periods of time (for two hours, for years)
◉ Use “since” for points in time (since Monday, since 2010)
Real-Life Present Tense Examples – Grouped by Use Case
It’s not enough to memorize grammar—you have to see it in action. Here are examples from real contexts that show how the present tense helps you express yourself clearly.
Examples of Simple Present Tense
◉ I wake up at 6 a.m.
◉ He studies French on weekends.
◉ The library opens at 9 o’clock.
◉ Does she enjoy cooking?
◉ They don’t like spicy food.
Examples of Present Continuous Tense
◉ She is talking to her friend.
◉ Are you watching the new series?
◉ I am not feeling well today.
◉ They are building a new school nearby.
◉ We are learning English grammar right now.
Examples of Present Perfect Tense
◉ I have already finished my homework.
◉ She has visited Paris three times.
◉ Have they eaten yet?
◉ He hasn’t called me back.
◉ We have lived here for a long time.
Examples of Present Perfect Continuous Tense
◉ I have been waiting for you since noon.
◉ She has been working at the same company for five years.
◉ Has he been practicing the guitar?
◉ We have been watching the rain all evening.
◉ They have not been sleeping well lately.
Present Tense Exercise with Answers
Use these exercises to practice what you’ve learned. Try not to scroll to the answers right away!
Fill in the blanks using the correct present tense form:
-
He __________ (write) emails to clients every day.
-
I __________ (read) a great book right now.
-
They __________ (not finish) their lunch yet.
-
She __________ (study) since morning.
-
We __________ (go) to the gym every Monday.
-
__________ you __________ (see) the latest movie?
-
It __________ (rain) a lot this week.
-
I __________ (not sleep) well lately.
-
__________ he always __________ (forget) his keys?
-
The baby __________ (cry) loudly.
Answer Key:
-
writes
-
am reading
-
have not finished
-
has been studying
-
go
-
Have, seen
-
has been raining
-
have not been sleeping
-
Does, forget
-
is crying
FAQs on Present Tense Chart with Examples
What is the simple present tense chart?
The simple present tense chart shows how verbs change based on the subject. It highlights when to add s/es for third-person singular and keeps the base form for all other subjects. For example:
-
I/You/We/They – play, eat, run
-
He/She/It – plays, eats, runs
The chart makes it easier to understand subject-verb agreement at a glance.
Can you share a complete present tense chart with examples?
Yes! A present tense chart with examples shows how each form of the present tense is structured and used. It includes:
-
Simple Present – I eat breakfast.
-
Present Continuous – She is eating breakfast.
-
Present Perfect – We have eaten already.
-
Present Perfect Continuous – They have been eating since morning.
This chart helps learners compare and apply each tense easily.
What are some good present tense examples?
Here are a few present tense examples from real-life situations:
-
Simple Present: He drives to work every day.
-
Present Continuous: I am reading a novel.
-
Present Perfect: She has finished her assignment.
-
Present Perfect Continuous: We have been talking for an hour.
These examples show how each tense works in natural conversation.
What is the correct present tense structure?
Each form has its own present tense structure:
-
Simple Present: Subject + base verb (+s/es)
-
Present Continuous: Subject + am/is/are + verb-ing
-
Present Perfect: Subject + have/has + past participle
-
Present Perfect Continuous: Subject + have/has been + verb-ing
Using the correct structure helps form accurate and fluent sentences.
What does simple present tense mean?
The simple present tense describes actions that happen regularly, facts, habits, or scheduled events. It is the most basic and commonly used verb tense in English.
Example: The sun rises in the east.
Can you give some simple present tense examples?
Certainly! Here are some simple Present Tense Chart with Examples:
-
I walk to school every day.
-
She plays the piano beautifully.
-
They live in Canada.
-
The train leaves at 6 p.m.
These examples reflect habits, truths, and repeated actions.
What is the simple present tense formula?
The simple present tense formula is:
-
Affirmative: Subject + base verb (+s/es)
-
Negative: Subject + do/does not + base verb
-
Interrogative: Do/Does + subject + base verb?
This formula helps construct correct and meaningful simple present sentences.
Conclusion on Present tense chart with examples
Think about how often you talk about your daily routine, share facts, or describe what’s happening around you—that’s the present tense in action. This guide has given you a clear and practical way to use it with the help of a detailed present tense chart with examples. You’ve seen real sentences, learned the correct structures, and discovered how each tense fits different situations.
Using this present tense chart with examples as a reference can make your speaking and writing smoother and more accurate. Keep it handy, apply it in real-life conversations, and you’ll notice real improvement. With a bit of daily practice, grammar becomes less of a rulebook and more of a tool to express yourself confidently.

