Direct and indirect speech exercises are essential for English learners who want to master the art of reporting what someone else has said. Understanding how to convert direct speech into indirect speech and vice versa can help improve both your speaking and writing skills. Let’s dive into the basics of direct and indirect speech and go through some helpful exercises to solidify your understanding. So start to learn direct and indirect speech exercises.
What is Direct Speech?
Direct speech is when we repeat the exact words spoken by someone. It is usually placed inside quotation marks. For example:
- He said, “I am going to the market.”
What is Indirect Speech?
Indirect speech, on the other hand, is when we report someone’s words without quoting them directly. Instead, we convey the message or the meaning of what was said, using a reporting verb like “said,” “told,” or “asked.”
For example:
- He said he was going to the market.
Rules of Changing Direct and Indirect Speech
- Change of Pronouns: The pronouns in the direct speech are changed in the indirect speech. For example, “I” becomes “he/she,” “we” becomes “they,” and “you” becomes “he/she/they” depending on context.
- Tense Change: The tense usually shifts one step back in time.
- Present Simple → Past Simple
- Present Continuous → Past Continuous
- Present Perfect → Past Perfect
- Past Simple → Past Perfect
- Omitting Quotation Marks: In indirect speech, we don’t use quotation marks.
- Using Reporting Verbs: In indirect speech, we use verbs like “said,” “told,” “asked,” etc., before the speech.
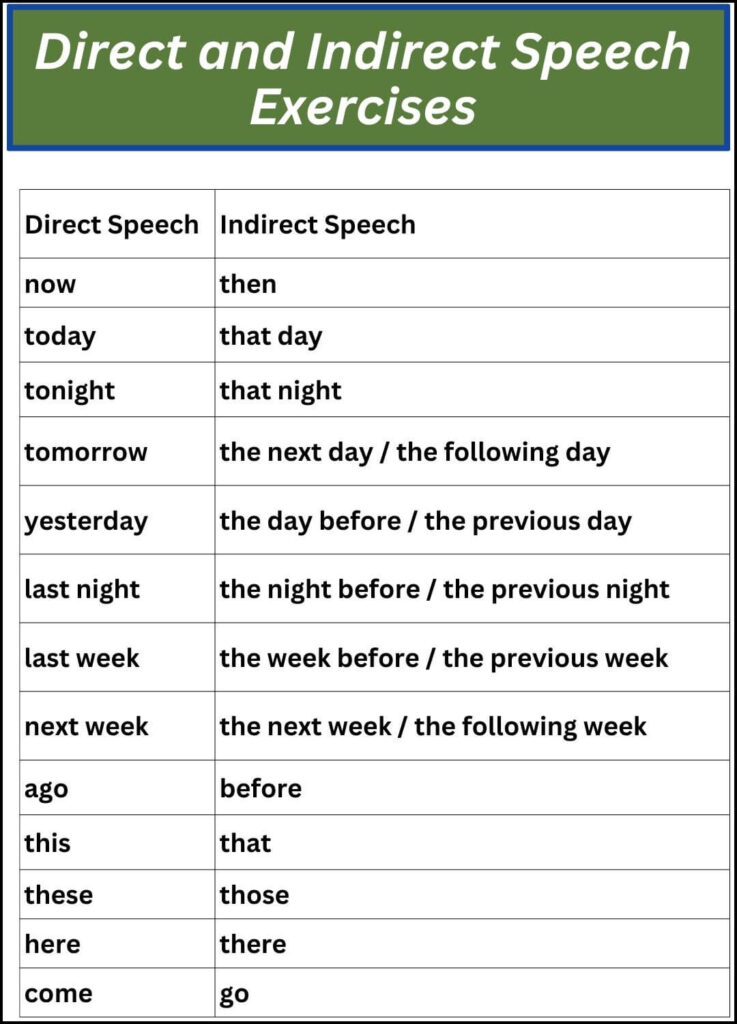
- Time Expressions: Words like “today,” “tomorrow,” “yesterday” may change when transforming direct speech to indirect speech.
| Direct Speech | Indirect Speech |
|---|---|
| now | then |
| today | that day |
| tonight | that night |
| tomorrow | the next day / the following day |
| yesterday | the day before / the previous day |
| last night | the night before / the previous night |
| last week | the week before / the previous week |
| next week | the next week / the following week |
| ago | before |
| this | that |
| these | those |
| here | there |
| come | go |
Changing Direct Speech into Indirect Speech
change the direct speech into indirect speech: Q1
- Direct Speech: She said, “I am reading a book.” Indirect Speech: She said that she was reading a book.
- Direct Speech: “I will go to the park tomorrow,” he said. Indirect Speech: He said that he would go to the park the next day.
- Direct Speech: “We are watching a movie,” they said. Indirect Speech: They said that they were watching a movie.
- Direct Speech: “I have finished my homework,” she said. Indirect Speech: She said that she had finished her homework.
- Direct Speech: “He will arrive soon,” she said. Indirect Speech: She said that he would arrive soon.
- Direct Speech: “I cannot find my keys,” John said. Indirect Speech: John said that he could not find his keys.
- Direct Speech: “I am going to the gym,” Mark said. Indirect Speech: Mark said that he was going to the gym.
- Direct Speech: “They are studying for their exams,” she said. Indirect Speech: She said that they were studying for their exams.
- Direct Speech: “I don’t like this song,” he said. Indirect Speech: He said that he didn’t like that song.
- Direct Speech: “We have been working all day,” they said. Indirect Speech: They said that they had been working all day.
- Direct Speech: “She is singing beautifully,” he said. Indirect Speech: He said that she was singing beautifully.
- Direct Speech: “I will call you later,” he said. Indirect Speech: He said that he would call me later.
- Direct Speech: “I am learning to play the guitar,” she said. Indirect Speech: She said that she was learning to play the guitar.
- Direct Speech: “It is raining outside,” he said. Indirect Speech: He said that it was raining outside.
- Direct Speech: “I am visiting my parents this weekend,” she said. Indirect Speech: She said that she was visiting her parents that weekend.
- Direct Speech: “We are going on holiday next month,” they said. Indirect Speech: They said that they were going on holiday the next month.
- Direct Speech: “I don’t know the answer,” she said. Indirect Speech: She said that she didn’t know the answer.
- Direct Speech: “He is reading a newspaper,” she said. Indirect Speech: She said that he was reading a newspaper.
- Direct Speech: “I will meet you at the cafe,” she said. Indirect Speech: She said that she would meet me at the cafe.
- Direct Speech: “I can’t make it to the party,” he said. Indirect Speech: He said that he couldn’t make it to the party.
Changing Indirect Speech into Direct Speech
Let’s practice changing indirect speech back into direct speech: Q2
- Indirect Speech: She said that she was reading a book. Direct Speech: “I am reading a book,” she said.
- Indirect Speech: He said that he would go to the park the next day. Direct Speech: “I will go to the park tomorrow,” he said.
- Indirect Speech: They said that they were watching a movie. Direct Speech: “We are watching a movie,” they said.
- Indirect Speech: She said that she had finished her homework. Direct Speech: “I have finished my homework,” she said.
- Indirect Speech: He said that he would arrive soon. Direct Speech: “He will arrive soon,” she said.
- Indirect Speech: John said that he could not find his keys. Direct Speech: “I cannot find my keys,” John said.
- Indirect Speech: Mark said that he was going to the gym. Direct Speech: “I am going to the gym,” Mark said.
- Indirect Speech: She said that they were studying for their exams. Direct Speech: “They are studying for their exams,” she said.
- Indirect Speech: He said that he didn’t like that song. Direct Speech: “I don’t like this song,” he said.
- Indirect Speech: They said that they had been working all day. Direct Speech: “We have been working all day,” they said.
- Indirect Speech: He said that she was singing beautifully. Direct Speech: “She is singing beautifully,” he said.
- Indirect Speech: He said that he would call me later. Direct Speech: “I will call you later,” he said.
- Indirect Speech: She said that she was learning to play the guitar. Direct Speech: “I am learning to play the guitar,” she said.
- Indirect Speech: He said that it was raining outside. Direct Speech: “It is raining outside,” he said.
- Indirect Speech: She said that she was visiting her parents that weekend. Direct Speech: “I am visiting my parents this weekend,” she said.
- Indirect Speech: They said that they were going on holiday the next month. Direct Speech: “We are going on holiday next month,” they said.
- Indirect Speech: She said that she didn’t know the answer. Direct Speech: “I don’t know the answer,” she said.
- Indirect Speech: She said that he was reading a newspaper. Direct Speech: “He is reading a newspaper,” she said.
- Indirect Speech: She said that she would meet me at the cafe. Direct Speech: “I will meet you at the cafe,” she said.
- Indirect Speech: He said that he couldn’t make it to the party. Direct Speech: “I can’t make it to the party,” he said.
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises
Lets learn about chaning naration with direct and indirect speech exercises –
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises 1
Change the following direct speech into indirect speech:
- “I am tired,” she said.
- “We will arrive at noon,” they said.
- “She is playing tennis,” he said.
- “I am waiting for my friend,” he said.
- “They are going on a trip,” she said.
Answers:
- She said that she was tired.
- They said that they would arrive at noon.
- He said that she was playing tennis.
- He said that he was waiting for his friend.
- She said that they were going on a trip.
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises 2
Change the following indirect speech into direct speech:
- He said that he was going to the library.
- She said that she would help me.
- They said that they had completed the project.
- John said that he didn’t like the movie.
- She said that she was feeling ill.
Answers:
- “I am going to the library,” he said.
- “I will help you,”
3. “We have completed the project,” they said.
4. “I don’t like the movie,” John said.
5. “I am feeling ill,” she said.
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises 3
Change the following direct speech into indirect speech:
- “I can’t attend the meeting,” she said.
- “I have been to France,” he said.
- “We will visit you tomorrow,” they said.
- “I am learning to cook,” she said.
- “He has already left,” she said.
Answers:
- She said that she couldn’t attend the meeting.
- He said that he had been to France.
- They said that they would visit me the next day.
- She said that she was learning to cook.
- She said that he had already left.
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises 4
Change the following indirect speech into direct speech:
- He said that he could play the guitar.
- She said that she was studying for the test.
- They said that they would help us with the project.
- John said that he had never been to Italy.
- She said that she didn’t like chocolate.
Answers:
- “I can play the guitar,” he said.
- “I am studying for the test,” she said.
- “We will help you with the project,” they said.
- “I have never been to Italy,” John said.
- “I don’t like chocolate,” she said.
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises 5
Change the following direct speech into indirect speech:
- “I am going to bed early tonight,” she said.
- “We will arrive at 7 PM,” they said.
- “She is painting a picture,” he said.
- “I am going to watch a movie,” he said.
- “They are planning a trip,” she said.
Answers:
- She said that she was going to bed early that night.
- They said that they would arrive at 7 PM.
- He said that she was painting a picture.
- He said that he was going to watch a movie.
- She said that they were planning a trip.
FAQs About Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises
1. What is the main difference between direct and indirect speech?
The main difference is that direct speech quotes the exact words of the speaker, while indirect speech reports the meaning of what was said without quoting it directly. For example, direct speech is, “I am going to the park,” while indirect speech is, “He said that he was going to the park.”
2. When do we change the tense while converting direct speech into indirect speech?
Generally, we change the tense when the reporting verb is in the past tense. For example, if the direct speech is in the present tense, it will usually change to the past tense in indirect speech.
3. Can we leave out quotation marks in indirect speech?
Yes, quotation marks are not used in indirect speech. Instead, we use the word “that” (optional in some cases) to connect the reporting verb and the reported speech.

