Understanding verb forms is essential for mastering English grammar. Whether you’re a student preparing for exams, a professional improving your writing skills, or someone learning English as a second language, knowing how verbs transform across different tenses and contexts will dramatically improve your command of the language.
The Foundation of English Verb Forms v1 v2 v3 v4 v5
English verbs are remarkably versatile, taking on different forms to express time, action, and relationships in our sentences. These forms, commonly known as V1, V2, V3, V4, and V5, serve as building blocks for constructing clear and effective communication.
Understanding the Five Verb Forms v1 v2 v3 v4 v5
Let’s break down each verb form to understand its unique role in English grammar:
Base Form (V1)
The base form, or V1, is the fundamental version of the verb as found in the dictionary. It’s used in several ways:
- The base form appears in simple present tense with I, you, we, and they
- It’s essential for forming infinitives with “to”
- This form creates imperatives or commands
- It combines with auxiliary verbs like “do” and “will”
Simple Past (V2)
The second verb form represents actions completed in the past:
- Regular verbs form V2 by adding “-ed” to the base form
- Irregular verbs have unique past forms that must be memorized
- This form stands alone without helping verbs
- It describes specific actions at a defined point in past time
Past Participle (V3)
The third form serves multiple functions:
- It combines with “have,” “has,” and “had” to form perfect tenses
- This form appears in passive voice constructions
- Regular verbs match their V2 form
- Many irregular verbs have distinct V3 forms
Present Third Person Singular (V4)
The fourth form occurs in specific present tense situations:
- Used exclusively with he, she, and it
- Usually formed by adding “-s” or “-es” to the base form
- Special spelling rules apply for certain word endings
- Demonstrates subject-verb agreement in present tense
Present Participle (V5)
The fifth form adds “-ing” to create:
- Continuous tenses with helping verbs
- Gerunds functioning as nouns
- Participial phrases modifying other sentence elements
- Progressive aspects of various tenses
Essential Verb Forms v1 v2 v3 v4 v5 Reference Tables
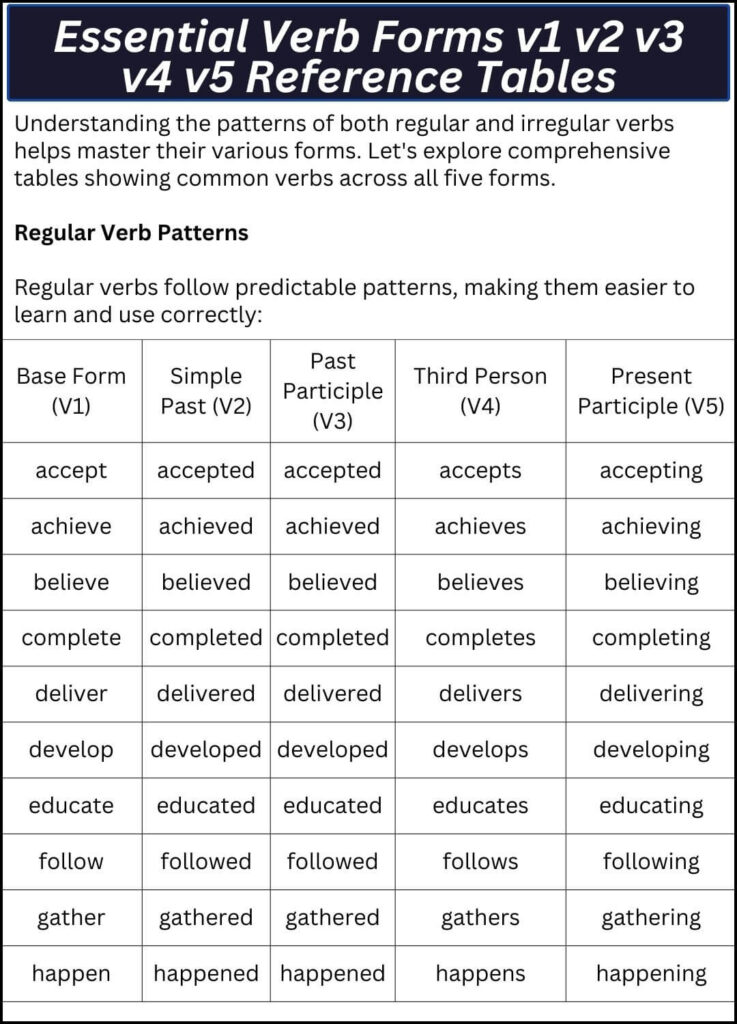
Understanding the patterns of both regular and irregular verbs helps master their various forms. Let’s explore comprehensive tables showing common verbs across all five forms.
Regular Verb Patterns
Regular verbs follow predictable patterns, making them easier to learn and use correctly:
| Base Form (V1) | Simple Past (V2) | Past Participle (V3) | Third Person (V4) | Present Participle (V5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| accept | accepted | accepted | accepts | accepting |
| achieve | achieved | achieved | achieves | achieving |
| believe | believed | believed | believes | believing |
| complete | completed | completed | completes | completing |
| deliver | delivered | delivered | delivers | delivering |
| develop | developed | developed | develops | developing |
| educate | educated | educated | educates | educating |
| follow | followed | followed | follows | following |
| gather | gathered | gathered | gathers | gathering |
| happen | happened | happened | happens | happening |
Common Irregular Verb Forms v1 v2 v3 v4 v5
Irregular verbs require special attention as they don’t follow standard patterns:
| Base Form (V1) | Simple Past (V2) | Past Participle (V3) | Third Person (V4) | Present Participle (V5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| begin | began | begun | begins | beginning |
| break | broke | broken | breaks | breaking |
| choose | chose | chosen | chooses | choosing |
| draw | drew | drawn | draws | drawing |
| eat | ate | eaten | eats | eating |
| fly | flew | flown | flies | flying |
| grow | grew | grown | grows | growing |
| hide | hid | hidden | hides | hiding |
| know | knew | known | knows | knowing |
| lead | led | led | leads | leading |
Special Cases and Pattern Recognition
Understanding these special cases helps master verb forms:
Double Letter Patterns
- When a single-syllable verb ends in consonant + vowel + consonant:
- Double the final consonant before adding -ed or -ing
- Examples: stop → stopped/stopping, plan → planned/planning
Words Ending in ‘e’
- For verbs ending in ‘e’:
- Drop the ‘e’ before adding -ing
- Just add ‘d’ for past forms
- Examples: write → writing/wrote/written, take → taking/took/taken
‘Y’ to ‘I’ Changes
- When a verb ends in consonant + y:
- Change ‘y’ to ‘i’ before adding -es, -ed
- Keep ‘y’ when adding -ing
- Examples: try → tries/tried/trying, study → studies/studied/studying
100 Verb Forms v1 v2 v3 v4 v5
| Base Form (V1) | Simple Past (V2) | Past Participle (V3) | Third Person (V4) | Present Participle (V5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| accept | accepted | accepted | accepts | accepting |
| act | acted | acted | acts | acting |
| add | added | added | adds | adding |
| agree | agreed | agreed | agrees | agreeing |
| allow | allowed | allowed | allows | allowing |
| ask | asked | asked | asks | asking |
| be | was/were | been | is | being |
| become | became | become | becomes | becoming |
| begin | began | begun | begins | beginning |
| believe | believed | believed | believes | believing |
| break | broke | broken | breaks | breaking |
| bring | brought | brought | brings | bringing |
| build | built | built | builds | building |
| buy | bought | bought | buys | buying |
| call | called | called | calls | calling |
| carry | carried | carried | carries | carrying |
| catch | caught | caught | catches | catching |
| change | changed | changed | changes | changing |
| choose | chose | chosen | chooses | choosing |
| come | came | come | comes | coming |
| continue | continued | continued | continues | continuing |
| create | created | created | creates | creating |
| cut | cut | cut | cuts | cutting |
| decide | decided | decided | decides | deciding |
| do | did | done | does | doing |
| draw | drew | drawn | draws | drawing |
| drink | drank | drunk | drinks | drinking |
| drive | drove | driven | drives | driving |
| eat | ate | eaten | eats | eating |
| end | ended | ended | ends | ending |
| enjoy | enjoyed | enjoyed | enjoys | enjoying |
| explain | explained | explained | explains | explaining |
| fall | fell | fallen | falls | falling |
| feel | felt | felt | feels | feeling |
| find | found | found | finds | finding |
| finish | finished | finished | finishes | finishing |
| fly | flew | flown | flies | flying |
| follow | followed | followed | follows | following |
| forget | forgot | forgotten | forgets | forgetting |
| get | got | got/gotten | gets | getting |
| give | gave | given | gives | giving |
| go | went | gone | goes | going |
| grow | grew | grown | grows | growing |
| happen | happened | happened | happens | happening |
| have | had | had | has | having |
| hear | heard | heard | hears | hearing |
| help | helped | helped | helps | helping |
| hide | hid | hidden | hides | hiding |
| hit | hit | hit | hits | hitting |
| hold | held | held | holds | holding |
| hope | hoped | hoped | hopes | hoping |
| hurt | hurt | hurt | hurts | hurting |
| keep | kept | kept | keeps | keeping |
| know | knew | known | knows | knowing |
| learn | learned/learnt | learned/learnt | learns | learning |
| leave | left | left | leaves | leaving |
| let | let | let | lets | letting |
| like | liked | liked | likes | liking |
| listen | listened | listened | listens | listening |
| live | lived | lived | lives | living |
| look | looked | looked | looks | looking |
| lose | lost | lost | loses | losing |
| make | made | made | makes | making |
| mean | meant | meant | means | meaning |
| meet | met | met | meets | meeting |
| move | moved | moved | moves | moving |
| need | needed | needed | needs | needing |
| open | opened | opened | opens | opening |
| pay | paid | paid | pays | paying |
| play | played | played | plays | playing |
| put | put | put | puts | putting |
| read | read | read | reads | reading |
| remember | remembered | remembered | remembers | remembering |
| run | ran | run | runs | running |
| say | said | said | says | saying |
| see | saw | seen | sees | seeing |
| sell | sold | sold | sells | selling |
| send | sent | sent | sends | sending |
| set | set | set | sets | setting |
| show | showed | shown | shows | showing |
| sing | sang | sung | sings | singing |
| sit | sat | sat | sits | sitting |
| sleep | slept | slept | sleeps | sleeping |
| speak | spoke | spoken | speaks | speaking |
| spend | spent | spent | spends | spending |
| stand | stood | stood | stands | standing |
| start | started | started | starts | starting |
| stop | stopped | stopped | stops | stopping |
| study | studied | studied | studies | studying |
| take | took | taken | takes | taking |
| talk | talked | talked | talks | talking |
| teach | taught | taught | teaches | teaching |
| tell | told | told | tells | telling |
| think | thought | thought | thinks | thinking |
| try | tried | tried | tries | trying |
| turn | turned | turned | turns | turning |
| understand | understood | understood | understands | understanding |
| use | used | used | uses | using |
| wait | waited | waited | waits | waiting |
| walk | walked | walked | walks | walking |
| want | wanted | wanted | wants | wanting |
| watch | watched | watched | watches | watching |
| win | won | won | wins | winning |
| work | worked | worked | works | working |
| write | wrote | written | writes |
Mastering Verb Forms v1 v2 v3 v4 v5 Usage in Context
Understanding how to use each verb form in real-world situations is crucial for effective communication. Let’s explore practical applications and common scenarios for each form.
Base Form (V1) in Action
The base form serves multiple functions in everyday language:
- With Modal Verbs
- I will write a letter
- She can swim well
- They must finish the project
- In Infinitive Form
- To walk in the rain
- To speak multiple languages
- To understand complex concepts
- Present Simple (except third person)
- I walk to work every day
- We write weekly reports
- They understand the requirements
Past Forms (V2 & V3) Usage Guidelines
Understanding when to use V2 (Simple Past) versus V3 (Past Participle):
Simple Past (V2) Examples
- Yesterday, I walked to the store
- Last week, she wrote an article
- They bought a new car last month
Past Participle (V3) Applications
- Perfect Tenses:
- I have written the report
- She has studied French
- They had completed the task
- Passive Voice:
- The letter was written yesterday
- The project has been completed
- The rules were broken
Third Person Singular (V4) Rules
Common spelling patterns for forming V4:
- Add -s to most verbs:
- run → runs
- play → plays
- sing → sings
- Add -es after:
- Sibilant sounds (ss, sh, ch, x, z):
- pass → passes
- watch → watches
- fix → fixes
- Consonant + o:
- go → goes
- do → does
- Sibilant sounds (ss, sh, ch, x, z):
- Change y to i and add -es:
- study → studies
- try → tries
- carry → carries
Present Participle (V5) Formation
Key rules for creating and using V5 forms:
- Basic Formation:
- Add -ing to base form:
- walk → walking
- play → playing
- sing → singing
- Add -ing to base form:
- Special Spelling Rules:
- Double final consonant:
- run → running
- sit → sitting
- stop → stopping
- Drop final -e:
- write → writing
- dance → dancing
- smile → smiling
- Double final consonant:
- Common Uses:
- Continuous tenses:
- I am writing
- She was walking
- They are studying
- Gerunds:
- Swimming is good exercise
- Reading improves vocabulary
- Learning never stops
- Continuous tenses:
Advanced Concepts and Common Challenges
Mastering Complex Verb Forms v1 v2 v3 v4 v5 Combinations
Understanding how different verb forms work together creates more sophisticated expression:
Perfect Continuous Combinations
- Present Perfect Continuous
- I have been working (have + been + V5)
- She has been studying (has + been + V5)
- Past Perfect Continuous
- They had been traveling (had + been + V5)
- We had been waiting (had + been + V5)
Passive Voice Constructions
- Present Passive
- The letter is written (is + V3)
- The songs are sung (are + V3)
- Past Passive
- The building was constructed (was + V3)
- The rules were followed (were + V3)
Troubleshooting Common Verb Forms v1 v2 v3 v4 v5 Mistakes
Regular vs. Irregular Confusion
- Common Error: “I goed to the store”
- Correct: “I went to the store”
- Remember: Irregular verbs don’t follow the standard -ed pattern
Subject-Verb Agreement Issues
- Common Error: “She write letters”
- Correct: “She writes letters”
- Remember: Third-person singular requires V4 form
Participle Problems
- Common Error: “I am went”
- Correct: “I am going”
- Remember: Continuous tenses always use V5 (ing form)
Tips for Mastering Verb Forms
- Practice Pattern Recognition
- Group verbs by similar patterns
- Create memory aids for irregular verbs
- Use repetition to reinforce learning
- Context-Based Learning
- Study verbs in real sentences
- Read extensively to see forms in action
- Practice writing in different tenses
- Progressive Learning Strategy
- Start with regular verbs
- Add irregular verbs gradually
- Master one tense before moving to the next
Conclusion
Mastering the five Verb Forms v1 v2 v3 v4 v5 opens the door to precise and effective communication in English. While the system may seem complex at first, understanding these patterns and practicing their use will naturally improve your language skills. Remember that even native speakers occasionally make mistakes with irregular verbs, so patience and consistent practice are key to success.
Keep this guide handy as a reference while you continue to develop your English language skills. With time and practice, using the correct verb forms will become second nature, allowing you to express yourself confidently in any situation.

