In the English language, certain suffixes, like “-ment,” play an important role in transforming words to convey different meanings. The suffix “-ment” is used to form nouns, typically denoting an action, process, or result. By attaching “-ment” to verbs, it creates a noun that helps describe the action itself or its consequences. Whether you’re a student, an aspiring writer, or simply curious about language, understanding words that end with “-ment” can significantly expand your vocabulary.
What Does the Suffix “MENT” Mean?
The suffix “-ment” comes from Latin, where it was used to indicate the result or product of an action. In modern English, “-ment” is commonly used to turn verbs into nouns, and these new nouns typically refer to the action, state, or result of something.
Key Characteristics of “-ment” Words:
- Action or Process: Many “-ment” words refer to an action or process that has been carried out.
- State or Condition: Some words reflect a state of being or condition.
- Result or Outcome: Others indicate the result or consequence of an action.
Here are some common examples of “-ment” words:
- Achievement: The result of accomplishing something.
- Agreement: The process or result of reaching a mutual decision.
- Enjoyment: The state of experiencing joy or pleasure.
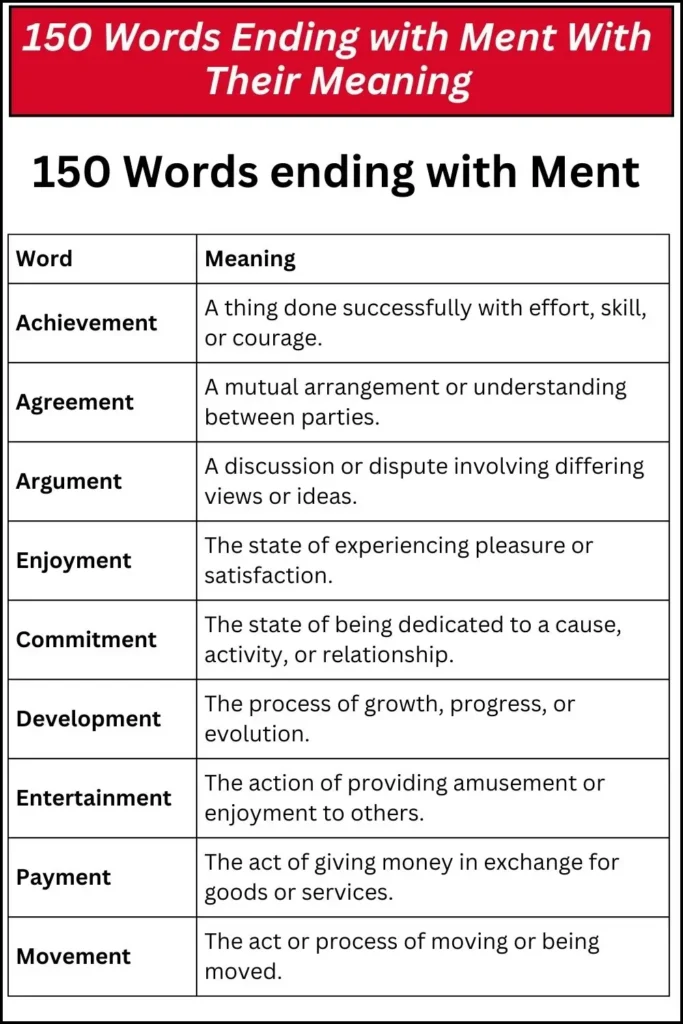
150 Words ending with Ment
| Word | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Achievement | A thing done successfully with effort, skill, or courage. |
| Agreement | A mutual arrangement or understanding between parties. |
| Argument | A discussion or dispute involving differing views or ideas. |
| Enjoyment | The state of experiencing pleasure or satisfaction. |
| Commitment | The state of being dedicated to a cause, activity, or relationship. |
| Development | The process of growth, progress, or evolution. |
| Entertainment | The action of providing amusement or enjoyment to others. |
| Payment | The act of giving money in exchange for goods or services. |
| Movement | The act or process of moving or being moved. |
| Management | The process of planning, organizing, and overseeing activities. |
| Government | The group of people responsible for overseeing the management of a country, state, or organization. |
| Investment | The action or process of putting money into something to gain a return. |
| Disappointment | The feeling of sadness or dissatisfaction caused by an unmet expectation. |
| Statement | A clear expression of something in speech or writing. |
| Improvement | The process of making something better or more effective. |
| Adjustment | The process of changing or altering something to fit new conditions. |
| Announcement | The act of publicly making information known. |
| Establishment | The process of founding or creating something; or the institution created. |
| Abandonment | The act of leaving someone or something behind, typically without care. |
| Embellishment | The process of adding decorative features to something. |
| Confirmation | The act of verifying or affirming the truth or correctness of something. |
| Fulfillment | The achievement of something desired, promised, or predicted. |
| Alignment | The arrangement in a straight line or in proper relative positions. |
| Settlement | The process of reaching an agreement or arrangement, typically in law. |
| Excitement | The feeling of enthusiasm or eagerness. |
| Recruitment | The process of finding and hiring new employees. |
| Encouragement | The act of giving someone confidence or support. |
| Nourishment | The process of providing the food necessary for growth and health. |
| Argumentation | The process or art of presenting arguments. |
| Experimentation | The act of conducting tests or experiments. |
| Abetment | The act of encouraging or assisting someone to do something illegal. |
| Acknowledgment | The act of recognizing or accepting something. |
| Annulment | The formal declaration that something is invalid. |
| Banishment | The act of expelling someone from a place or group. |
| Bereavement | The state of having lost someone close to death. |
| Betterment | The process of improving something or someone. |
| Disbursement | The act of paying out money from a fund. |
| Disturbance | A disruption of normal activity or peace. |
| Endorsement | The act of publicly supporting or approving something. |
| Enlistment | The act of enrolling or signing up for service. |
| Entanglement | The state of being tangled or caught in something. |
| Excitement | A feeling of great enthusiasm and eagerness. |
| Enforcement | The act of ensuring that laws or rules are followed. |
| Enlightenment | The state of being enlightened or gaining knowledge. |
| Entitlement | The right to have or do something. |
| Establishment | The process of setting up an organization or institution. |
| Expenditure | The action of spending funds. |
| Disenchantment | The state of being disappointed or losing enthusiasm. |
| Fragmentation | The action of breaking something into pieces. |
| Fulfillment | The achievement or realization of a goal or wish. |
| Harassment | The act of subjecting someone to aggressive pressure or intimidation. |
| Impairment | The state of being damaged or weakened. |
| Improvement | The act or process of making something better. |
| Installation | The process of putting something in place or making it ready for use. |
| Management | The process of organizing and overseeing activities. |
| Measurement | The act or process of determining the size, amount, or degree of something. |
| Mismanagement | The act of managing something badly or inefficiently. |
| Movement | The process of changing position or place. |
| Notification | The action of informing or giving notice. |
| Ornamentation | The act of decorating something. |
| Overpayment | The act of paying more than the required amount. |
| Parchment | A type of paper made from animal skin, used especially in ancient times. |
| Proclamation | The public or official announcement of something. |
| Realignment | The process of changing or correcting the position of something. |
| Reinvestment | The action of reinvesting capital into a business or asset. |
| Settlement | The process of concluding or resolving a dispute or issue. |
| Superintendency | The act of supervising or overseeing an activity. |
| Unemployment | The state of being without a job or employment. |
| Underpayment | The action of paying less than the required amount. |
| Unemployment | The condition of being without a job. |
| Verification | The process of establishing the truth or accuracy of something. |
| Wonderment | A state of awe or amazement. |
| Acknowledgement | The recognition or acceptance of the truth or existence of something. |
| Accomplishment | The successful completion of a task or achievement. |
| Amendment | A formal change or addition to a document or law. |
| Arrangement | The process of organizing or setting up something. |
| Bereavement | The state of having lost someone through death. |
| Disappointment | A feeling of sadness or displeasure caused by the non-fulfillment of hopes. |
| Enforcement | The act of compelling observance of a law, rule, or obligation. |
| Establishment | The process of creating or setting up something. |
| Fragmentation | The action of breaking something into smaller pieces. |
The Impact of “-MENT” Words in English Communication
Words ending with Ment are widely used in everyday language, professional settings, and academic discourse. Understanding the formation and meaning of these words helps speakers and writers express ideas more clearly and precisely. Let’s break down the key roles these words play in communication.
Describing Processes and Actions: Many “-ment” words describe actions or processes, helping us convey what is being done or what is in progress. For instance, “development” refers to the process of growth or progress, while “commitment” signifies the dedication to an ongoing action.
Representing Results and Outcomes: The suffix “-ment” also indicates the result of an action. For example, “achievement” is the result of completing a task successfully, and “improvement” refers to the positive outcome of enhancing something. These words help describe not only what has been done but also the impact it has created.
Creating Nouns for Emotional States: Words ending in “-ment” can express emotional states. “Disappointment,” for instance, conveys a feeling of sadness or dissatisfaction, while “enjoyment” refers to a state of happiness or pleasure. These nouns allow us to talk about emotions and reactions in a more detailed and structured way.
Enhancing Formal Writing and Speech: “-ment” words are particularly useful in formal writing and speech. They help convey complex ideas more succinctly. Words like “management,” “investment,” and “government” are essential in business, economics, and political discussions.
Why Should You Care About Words Ending with MENT?
Learning and using Words ending with Ment can significantly improve your communication skills. Whether you’re writing an essay, participating in a meeting, or simply having a conversation, these words can help you express complex ideas in a clear and efficient manner.
Improves Vocabulary: Expanding your knowledge of “-ment” words enriches your vocabulary, helping you become a more effective communicator. The more you understand about how these words are formed, the more capable you become in using them appropriately in both written and spoken language.
Supports Clarity in Writing: Words like “statement,” “investment,” and “commitment” help convey precise meanings, particularly in formal settings such as business communication, academic writing, and legal discussions. They help convey ideas succinctly, preventing ambiguity.
Enhances Professional Communication: Many “-ment” words are commonly used in professional contexts, especially in business, law, and governance. Knowing how to use them effectively can make you sound more authoritative and polished in meetings, presentations, and professional discussions.
Conclusion On Words ending with Ment
Words Ending with Ment are an essential part of the English language, transforming verbs into nouns that express actions, states, processes, and results. By understanding these words and incorporating them into your vocabulary, you can enhance your ability to communicate more clearly and precisely. Whether you’re looking to improve your academic writing, engage in professional discourse, or simply enrich your language skills, mastering “-ment” words can help you achieve those goals.