Language is a powerful tool, and understanding its intricacies can elevate our communication skills. One fascinating aspect of English is the variety of verbs that end with T. These verbs not only add depth to our vocabulary but also play a crucial role in crafting sentences that convey precise meanings. In this article, we will delve into the world of Verbs that end with T exploring their significance, common examples, and how to use them effectively in sentences.
Verbs that end with T are part of a broader category of words that conclude with this letter, including nouns and adjectives. However, focusing on verbs allows us to examine how these words contribute to the dynamic nature of language. Whether you are a student looking to improve your grammar skills or a professional seeking to refine your writing, understanding these verbs is essential.
What Are Verbs That End with T?
Verbs are action words that express what is happening, has happened, or will happen. Verbs that end with T can be regular or irregular, depending on their past tense forms. Regular verbs typically form their past tense by adding “-ed,” but some verbs ending in “T” may follow different patterns. For instance, the verb “cut” remains “cut” in the past tense, while “bet” becomes “bet” as well. Understanding these patterns is crucial for effective communication.
Regular Verbs: These verbs form their past tense by adding “-ed” or “-d.”
Irregular Verbs: These verbs do not follow the standard pattern for forming the past tense.
Past Tense: The form of a verb used to describe actions that occurred in the past.
Common Words That End With T
Many verbs in English end with the letter “T,” and they are used frequently in everyday language. Here are a few examples:
Act
Bet
Cut
Get
Set
Let
These verbs are versatile and can be used in various contexts, from casual conversations to formal writing.
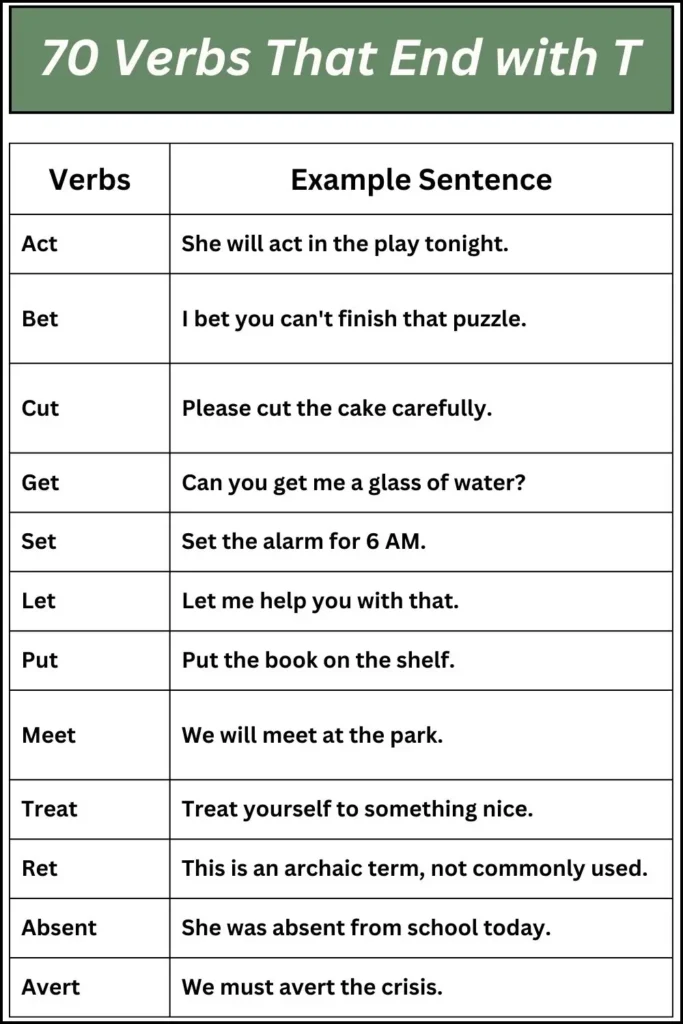
70 Verbs That End with T
Below is a table listing 70 verbs that end with T,” along with example sentences to illustrate their usage:
| Verbs | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Act | She will act in the play tonight. |
| Bet | I bet you can’t finish that puzzle. |
| Cut | Please cut the cake carefully. |
| Get | Can you get me a glass of water? |
| Set | Set the alarm for 6 AM. |
| Let | Let me help you with that. |
| Put | Put the book on the shelf. |
| Meet | We will meet at the park. |
| Treat | Treat yourself to something nice. |
| Ret | This is an archaic term, not commonly used. |
| Absent | She was absent from school today. |
| Accept | I accept your invitation. |
| Adapt | We need to adapt to the new rules. |
| Adopt | They decided to adopt a pet. |
| Alert | The alert system warned us of the storm. |
| Assist | Please assist me with this task. |
| Audit | The company will audit its accounts. |
| Avert | We must avert the crisis. |
| Avow | She avowed her love for him. |
| Beget | The king beget many sons. |
| Beset | The city was beset by problems. |
| Best | This is the best cake I’ve ever tasted. |
| Betray | He betrayed his friend’s trust. |
| Breat | This is an archaic term, not commonly used. |
| Burst | The balloon will burst if you squeeze it. |
| Cast | Cast your vote wisely. |
| Cat | This is not typically a verb ending in “T,” but can be used as one in certain contexts. |
| Cheat | Don’t cheat on the exam. |
| Chest | This is not typically a verb, but can be used as one in certain contexts. |
| Clot | The blood will clot soon. |
| Coat | Coat the chicken with sauce. |
| Commit | I commit to finishing this project. |
| Comport | She comported herself with dignity. |
| Confront | We must confront our fears. |
| Consent | I consent to the terms. |
| Contest | Let’s contest the election results. |
| Convert | Convert the file to PDF. |
| Cost | This is not typically a verb ending in “T,” but can be used as one in certain contexts. |
| Court | The court will hear the case. |
| Cutlet | This is not typically a verb, but can be used as one in certain contexts. |
| Dart | The dart flew straight. |
| Debit | The debit card was declined. |
| Defeat | We will defeat our opponents. |
| Defect | The product has a defect. |
| Deport | The government will deport the illegal immigrants. |
| Detect | Detect the problem early. |
| Detest | I detest broccoli. |
| Diet | She is on a diet. |
| Direct | Direct the play with care. |
| Disport | They disported themselves at the party. |
| Divert | Divert the traffic to avoid the accident. |
| Divest | We must divest our shares. |
| Docket | The docket was full of cases. |
| Doubt | I doubt his intentions. |
| Draft | Draft the letter carefully. |
| Drift | The boat will drift away if not anchored. |
| Drought | This is not typically a verb, but can be used as one in certain contexts. |
| Dust | Dust the furniture regularly. |
| Exert | Exert yourself to finish the task. |
| Exhort | The preacher exhorted the congregation. |
| Extort | They tried to extort money from him. |
| Fault | This is not typically a verb ending in “T,” but can be used as one in certain contexts. |
| Feint | The boxer feinted to distract his opponent. |
| Felt | This is the past tense of “feel,” but can be used as a verb ending in “T” in certain contexts. |
| Flout | They flouted the rules. |
| Gelt | This is not typically a verb, but can be used as one in certain contexts. |
| Get | Get the groceries from the store. |
| Gilt | This is not typically a verb, but can be used as one in certain contexts. |
| Hint | Give me a hint about the answer. |
| Hit | The ball hit the wall. |
| Hurt | The injury will hurt for a while. |
| Insert | Insert the key into the lock. |
| Insult | Don’t insult him. |
| Intert | This is not typically a verb, but can be used as one in certain contexts. |
| Jolt | The jolt of electricity shocked him. |
| Kilt | This is not typically a verb, but can be used as one in certain contexts. |
| Knot | Tie a knot in the rope. |
| Lament | We lament the loss of our friend. |
| Let | Let the dog out. |
| Lift | Lift the box carefully. |
| List | Make a list of the items. |
| Lit | This is the past tense of “light,” but can be used as a verb ending in “T” in certain contexts. |
| Meet | We will meet at the conference. |
| Melt | The ice will melt soon. |
| Merit | The proposal merits consideration. |
| Mint | Mint leaves are used in tea. |
| Misfit | The misfit in the group felt isolated. |
| Mist | Mist the plants regularly. |
| Moat | This is not typically a verb, but can be used as one in certain contexts. |
| Mount | Mount the bike on the rack. |
| Mourn | We mourn the loss of our loved one. |
| Must | You must try this cake. |
| Net | This is not typically a verb ending in “T,” but can be used as one in certain contexts. |
| Nut | Crack the nut open. |
| Omit | Omit the unnecessary details. |
| Outfit | The outfit was perfect for the occasion. |
| Outwit | Try to outwit your opponent. |
| Paint | Paint the room blue. |
| Part | Part the curtains to let in sunlight. |
| Pelt | Pelt the dog with treats. |
| Permit | Permit me to enter. |
| Pet | Pet the cat gently. |
| Pit | The pit in the ground was deep. |
| Plot | Plot the graph carefully. |
| Point | Point to the correct answer. |
| Port | The ship arrived at the port. |
| Post | Post the letter today. |
| Pout | The child began to pout. |
| Present | Present the gift to her. |
| Pret | This is not typically a verb, but can be used as one in certain contexts. |
| Print the document now. | |
| Profit | The company will profit from the deal. |
| Prompt | Prompt the actor to start speaking. |
| Put | Put the book on the shelf. |
| Quit | Quit smoking for your health. |
| Rent | Rent the apartment for a month. |
| Repast | The repast was delicious. |
| Repent | Repent for your sins. |
| Report | Report the incident to the police. |
| Repost | Repost the article on social media. |
| Result | The result of the test was surprising. |
| Retort | She retorted with a witty remark. |
| Revert | Revert to the previous version. |
| Rivet | Rivet the metal pieces together. |
| Rocket | The rocket soared into space. |
| Runt | This is not typically a verb, but can be used as one in certain contexts. |
| Rust | The metal will rust if not coated. |
| Set | Set the table for dinner. |
| Shunt | Shunt the train to the side track. |
| Skirt | Skirt around the issue. |
| Slant | Slant the roof to avoid snow accumulation. |
| Smart | This is not typically a verb ending in “T,” but can be used as one in certain contexts. |
| Smelt | This is the past tense of “smell,” but can be used as a verb ending in “T” in certain contexts. |
| Snout | This is not typically a verb, but can be used as one in certain contexts. |
| Sort | Sort the laundry before washing. |
| Spent | This is the past tense of “spend,” but can be used as a verb ending in “T” in certain contexts. |
| Sprint | Sprint to the finish line. |
| Sprout | The seeds will sprout soon. |
| Start | Start the car engine. |
| Stint | Stint on expenses to save money. |
| Stret | This is not typically a verb, but can be used as one in certain contexts. |
| Strut | Strut around the stage confidently. |
| Taunt | Don’t taunt the animal. |
| Teat | This is not typically a verb, but can be used as one in certain contexts. |
| Tempt | Tempt fate at your own risk. |
| Test | Test the product before launching. |
| Thwart | Thwart the plans to avoid trouble. |
| Tint | Tint the windows for privacy. |
| Toast | Toast the bread until it’s brown. |
| Tot | This is not typically a verb, but can be used as one in certain contexts. |
| Tout | Tout the benefits of the new product. |
| Treat | Treat yourself to a vacation. |
| Trust | Trust your instincts. |
| Turnout | This is not typically a verb, but can be used as one in certain contexts. |
| Twist | Twist the rope to make it stronger. |
| Unseat | Unseat the incumbent in the election. |
| Uproot | Uproot the weeds from the garden. |
| Upset | The news upset her. |
| Uptilt | This is not typically a verb, but can be used as one in certain contexts. |
| Vomit | Vomit if you feel nauseous. |
| Waft | Waft the scent through the air. |
| Want | I want to go home. |
| Weft | This is not typically a verb, but can be used as one in certain contexts. |
| Wet | The grass is wet from the rain. |
| Whet | Whet your appetite before dinner. |
| Wilt | The flowers will wilt without water. |
How to Use Verbs That End with T Correctly
Mastering verbs that end with “T” requires attention to their grammatical behavior and contextual usage. These verbs often follow irregular patterns, making them distinct from regular verbs. Below are key guidelines to ensure accurate usage:
Rules for Using Verbs Ending in T
Past Tense Formation:
Irregular Verbs: Many verbs ending in “T” retain their base form in the past tense (e.g., cut → cut, bet → bet).
Regular Verbs: Some add “-ed” (e.g., insert → inserted).
Exceptions: Verbs like set and let remain unchanged in the past tense (set → set, let → let).
Past Participle:
Use the past tense form for past participles (e.g., I have cut the grass).Tense Consistency:
Ensure verbs align with the sentence’s tense. For example:“She acts in plays, but yesterday she acted in a film.”
Modal Verbs:
Combine with modals like can, will, or must (e.g., You must set the table).
How Words That End With T Are Used in Sentences
Verbs ending in “T” appear in various sentence structures, from simple statements to complex clauses. Here’s how they function:
Common Sentence Patterns
Transitive Verbs: Require an object (e.g., She cut the ribbon).
Intransitive Verbs: Do not require an object (e.g., The balloon burst).
Phrasal Verbs: Combine with prepositions (e.g., Set up the tent).
Examples of Contextual Usage
| Verb | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Act | “The actor acts naturally in every scene.” |
| Bet | “I bet you can’t solve this puzzle.” |
| Commit | “She committed to the project.” |
| Detect | “The sensor detects anomalies.” |
| Outwit | “He outwitted his opponent.” |
20 Exercises on Verbs That End with T
Test your understanding with these fill-in-the-blank exercises:
She ______ the cake carefully. (cut)
I ______ you can’t finish that task. (bet)
We ______ the meeting for tomorrow. (set)
The company ______ its profits last year. (report)
He ______ the rules to win the game. (flout)
The flowers ______ without water. (wilt)
She ______ her voice to sound confident. (modulate)
The teacher ______ the students to study harder. (exhort)
The storm ______ the coastal towns. (beset)
They ______ the problem early. (detect)
The artist ______ the painting with care. (retouch)
The government ______ the illegal immigrants. (deport)
The child ______ the dog gently. (pet)
The team ______ the competition. (thwart)
The chef ______ the sauce to perfection. (adjust)
The lawyer ______ the case strongly. (argue)
The company ______ its shares. (divest)
The musician ______ the melody beautifully. (render)
The teacher ______ the lesson plan. (revise)
The athlete ______ the record. (break)
Conclusion on Verbs That End with T
Verbs That End with T are a dynamic group that enrich our language. By mastering their usage, past tense forms, and contextual applications, you can enhance your writing and speaking skills. Remember to practice regularly with exercises like those above to reinforce your understanding. Whether you’re a student or a professional, these verbs will help you communicate with precision and creativity.

