In English, verb tenses in grammar are essential for indicating when an action or event occurs. Whether an action has happened in the past, is happening now, or will happen in the future, verb tenses help us convey that information clearly. Mastering verb tenses is crucial for both writing and speaking, as it allows us to describe events in a structured, coherent way.
Verb tenses are more than just a form of words; they help us convey timelines, perspectives, and relationships between actions. In this article, we will explore verb tenses in grammar, covering everything from basic tense structures to complex combinations, and show you how to use them effectively in different contexts.
What are verb tenses?
Verb tenses are a grammatical feature that helps us understand the timing of an action or event. Tense shows whether the action has already happened, is happening, or will happen.
There are three primary tenses in English grammar:
Past tense—Indicates an action that has already happened.
Present tense—Indicates an action that is happening now or regularly.
Future tense—Indicates an action that will happen.
Each tense is further divided into different aspects that provide more specific details about the action. These aspects include:
Simple—Describes a single, straightforward action.
Progressive (Continuous)—Describes an ongoing action.
Perfect—Describes an action that was completed before a certain point.
Perfect Progressive—Describes an ongoing action that was completed before a specific time.
Understanding the structure of verb tenses and their aspects allows you to communicate more precisely in English, whether you’re narrating a story, explaining something, or simply making a statement.
Types of Verb Tenses
Each verb tense is used to describe different times and types of actions. Let’s break down the various tenses into three categories: past, present, and future.
Past Tense
The past tense is used to describe actions that have already occurred. There are four types of past tense constructions:
Simple Past Tense
This tense describes an action that happened and was completed in the past.Example: She visited the museum yesterday.
Past Perfect Tense
This tense is used to describe an action that was completed before another action or point in the past.Example: By the time we arrived, she had left.
Past Progressive Tense
This tense describes an action that was ongoing in the past.Example: They were studying when I called them.
Past Perfect Progressive Tense
This tense is used to describe an ongoing action that was happening before another event in the past.Example: She had been waiting for hours before the bus finally arrived.
Present Tense
The present tense is used to describe actions happening now or regularly. It has four different types:
Simple Present Tense
This tense describes a habitual action or something that is generally true.Example: She plays the piano every day.
Present Perfect Tense
This tense describes an action that started in the past and continues into the present or has an effect on the present.Example: I have lived here for five years.
Present Progressive Tense
This tense describes an action that is happening at this very moment.Example: They are reading a book right now.
Present Perfect Progressive Tense
This tense describes an ongoing action that started in the past and continues up to the present.Example: She has been working all day.
Future Tense
The future tense is used to describe actions that will happen. There are also four types of future tense constructions:
Simple Future Tense
This tense describes an action that will occur in the future.Example: He will visit his grandmother next week.
Future Perfect Tense
This tense is used to describe an action that will be completed before another action or time in the future.Example: By next week, they will have finished the project.
Future Progressive Tense
This tense describes an ongoing action that will occur in the future.Example: I will be attending the meeting tomorrow.
Future Perfect Progressive Tense
This tense describes an ongoing action that will continue up until a certain point in the future.Example: By next year, I will have been working here for five years.
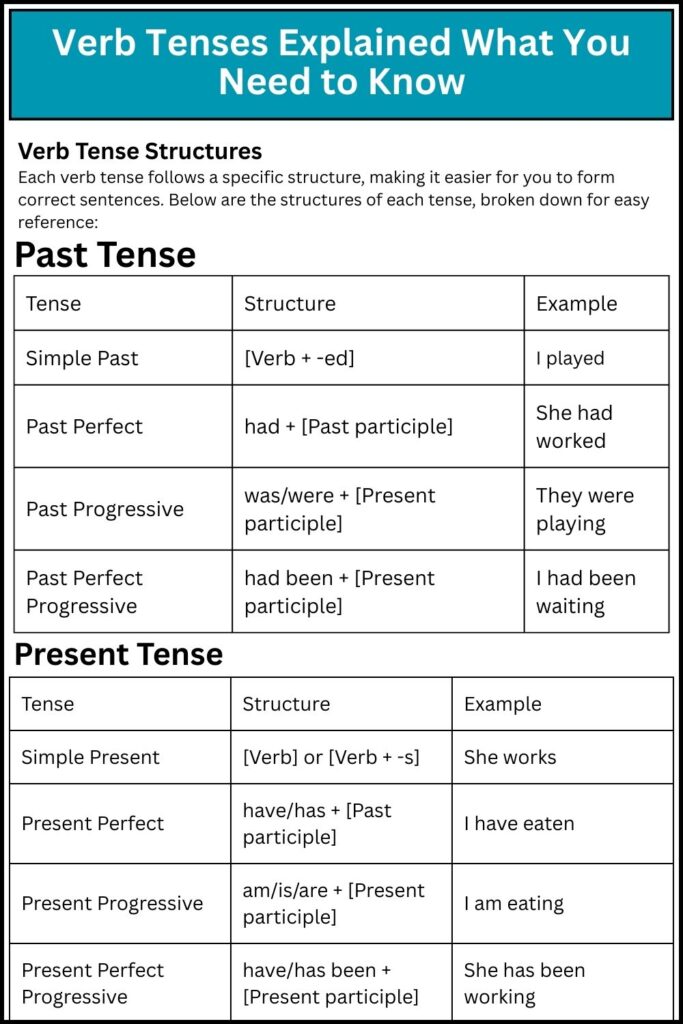
Verb Tense Structures
Each verb tense follows a specific structure, making it easier for you to form correct sentences. Below are the structures of each tense, broken down for easy reference:
Past Tense
| Tense | Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Past | [Verb + -ed] | I played |
| Past Perfect | had + [Past participle] | She had worked |
| Past Progressive | was/were + [Present participle] | They were playing |
| Past Perfect Progressive | had been + [Present participle] | I had been waiting |
Present Tense
| Tense | Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Present | [Verb] or [Verb + -s] | She works |
| Present Perfect | have/has + [Past participle] | I have eaten |
| Present Progressive | am/is/are + [Present participle] | I am eating |
| Present Perfect Progressive | have/has been + [Present participle] | She has been working |
Future Tense
| Tense | Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Future | will + [Verb] | They will eat |
| Future Perfect | will have + [Past participle] | I will have eaten |
| Future Progressive | will be + [Present participle] | I will be working |
| Future Perfect Progressive | will have been + [Present participle] | She will have been working |
How to Choose the Right Verb Tense
Choosing the correct verb tense depends on the context of the sentence. Ask yourself:
Is the action happening now, in the past, or in the future?
Is the action ongoing or completed?
Does the timing of the action relate to another event?
Once you determine the right time frame for the action, you can select the appropriate tense to communicate the information clearly.
Common Mistakes with Verb Tenses
Understanding verb tenses in grammar is crucial, but even experienced writers sometimes make mistakes. Here are some common errors to watch out for:
1. Incorrect Use of Tenses
One of the most common mistakes is using the wrong verb tense for the situation. For instance:
Incorrect: She will be studying tomorrow (should be “will study”).
Correct: She will study tomorrow.
Make sure that the tense you choose matches the timing of the action you’re describing. If you’re talking about a future event, use a future tense, like “will” or “going to,” and avoid using present tense unless you’re describing a future arrangement (e.g., The meeting starts at 10 AM tomorrow).
2. Shifting Tenses Inappropriately
Another frequent mistake is switching tenses unnecessarily within a sentence or paragraph. For example:
Incorrect: I was walking to the store when I see my friend (should be “saw”).
Correct: I was walking to the store when I saw my friend.
Avoid tense shifts unless there’s a clear reason to change the time frame of the action. Maintain consistency in your verb tenses to ensure clarity.
3. Confusing Present Perfect with Simple Past
The present perfect tense describes actions that started in the past and continue into the present or have relevance in the present. This can often be confused with simple past tense, which describes actions that are completed and disconnected from the present.
Incorrect: I visited New York last year (should be “visited”).
Correct: I visited New York last year.
If you’re referring to a specific time in the past, use the simple past tense. If the time is indefinite or has an effect on the present, use the present perfect.
4. Overusing Present Progressive
The present progressive tense describes actions that are happening at the moment of speaking or are ongoing. Sometimes, it’s overused, especially when the action is a general fact or routine. For example:
Incorrect: I am knowing her for five years (should be “have known”).
Correct: I have known her for five years.
For actions that are habitual or general, use the simple present, not the present progressive.
Conclusion
Mastering verb tenses in grammar is essential for clear and effective communication. Whether you are speaking or writing, the correct verb tense helps you convey the right meaning and make your sentences more precise. Understanding when to use the past, present, or future tenses and knowing how to express the aspect of the action ensures your language flows naturally and without confusion. With regular practice, you can improve your grasp of verb tenses and use them with confidence in all types of writing.

