Types of Adverbs in English Grammar and Their Explanation Adverbs Description(English):This guide introduces the many types, including manner, frequency, time, degree, way, and more, as well as how the types are made, and how to use them in a sentence.
Diving into Types of Adverbs
Adverbs are one of the most important parts of speech in the English language. Adverbs induce these modifications of parts of speech, and indicate how, when, where and to what degree an action is performed. This lesson will go one step back and continue further to learn about different types of adverbs in English grammar.
Adverbs of Manner
A manner adverb explains in what way something is done. They almost always end in -ly but there are exceptions. Adverbial — such as fast, cautious, and simply. Adverbs of manner — these types of adverbs express how an action takes place.
Example → She ran fast in order to catch the bus.
Adverbs of Time
Time adverbs tell us: when an action occurs. Such terms like yesterday, today, soon and now.
For instance, “I am going to call you tomorrow”.
Adverbs of Place
Place adverbs tell you where the action is taking place. This category also includes words like here, there, everywhere, and nearby.
For example: She searched high and low for her keys.
Adverbs of Frequency
These adverbs tell you what frequency an action happens. Examples include: always / never / often / rarely
He runs in the morning every time.
Adverbs of Degree
Adverbs of degree explain the intensity or extent of an action, adjective or another adverb. They consist of adverbs such as pretty, really, a little, and so.
Example: That movie was so exciting.
Adverbs of Probability
These adverbs refer to the possibility of an event or action happening. Adverbs of Probability are probably, certainly, likely & possibly.
FOR EXAMPLE: He’s likely to come to the party tonight.
Interrogative Adverbs
Some adverbs are used for grammatical purposes and some one of them is interrogative adverbs which are used to ask questions. Some of them are common ones i.e. why, when, where, how etc.
Make these into open-ended questions, Example — You left the party early, why?
Adverbs can be classified into various types based on their functions and meanings. Here are some common types of adverbs:
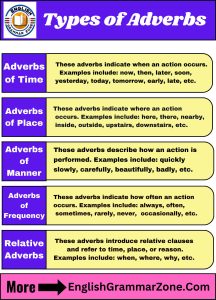
- Adverbs of Time: These adverbs indicate when an action occurs. Examples include: now, then, later, soon, yesterday, today, tomorrow, early, late, etc.
- Adverbs of Place: These adverbs indicate where an action occurs. Examples include: here, there, nearby, abroad, inside, outside, upstairs, downstairs, etc.
- Adverbs of Manner: These adverbs describe how an action is performed. Examples include: quickly, slowly, carefully, beautifully, loudly, quietly, well, badly, etc.
- Adverbs of Frequency: These adverbs indicate how often an action occurs. Examples include: always, often, sometimes, rarely, never, frequently, occasionally, etc.
- Adverbs of Degree or Intensity: These adverbs modify the intensity or degree of an action, adjective, or another adverb. Examples include: very, extremely, quite, rather, too, enough, almost, nearly, etc.
- Adverbs of Certainty or Probability: These adverbs express the speaker’s certainty or doubt about the action. Examples include: certainly, surely, probably, possibly, definitely, maybe, etc.
- Adverbs of Reason or Purpose: These adverbs explain why something happens or the purpose of an action. Examples include: therefore, consequently, thus, so, hence, accordingly, etc.
- Interrogative Adverbs: These adverbs are used to ask questions about time, place, manner, reason, etc. Examples include: when, where, how, why, etc.
- Relative Adverbs: These adverbs introduce relative clauses and refer to time, place, or reason. Examples include: when, where, why, etc.
- Conjunctive Adverbs: These adverbs connect clauses or sentences and show the relationship between them. Examples include: however, therefore, meanwhile, moreover, nevertheless, etc.
These are the main types of adverbs, each serving a specific purpose in modifying verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs in a sentence.

Additional Tips of Types of Adverbs
The overuse of adverbs can make sentences feel congested. Use adverbs sparingly — only when they convey important context or detail.
Double adverb: Do not use two words that modify the meaning of the same verb by means of adverbial manner of question as this could lead to redundancy of your sentence. That is because instead of saying “She ran very quickly,” we can say, “She ran quickly.”
Adverbs of degree are dangerous: they add strength to an adjective or a verb (very strong, too much) but too often, things become overstated (warning text, or warning, as far as the I would have known, do not dare)
Practice variety: Do not repeat the same adverb over and over, try using new, different adverbs.
Getting to the part with the adverbs with which you can modify your sentence to make it thicker and fuller and richer and connecting a reader to you in a way that your speaking is barely a human touch due to how emotive and engaging you can make it sound.
Conclusion
To sum up, if you are aware with which kind of adverbs exist and how they should be used, you would have no problem in communicating with those sentences with perfect clarity. Adverbs help you add relevant details to your writing and speech. It is essential for mastering English grammar — whether it be how, when, where, how often, or how much you are going to use an adverb.

