What is tense?
Tense refers to the grammatical category that shows the time of an action, event, or condition. It is used to express when an action occurs, whether in the past, present, or future. Each verb tense has a specific form and structure that conveys this information.
Types of Tenses
English has three main types of tenses, each divided into four aspects:
- Present Tense: Actions happening now.
- Past Tense: Actions that happened before now.
- Future Tense: Actions that will happen later.
Each of these is further categorized into four aspects:
- Simple: Basic form of the tense.
- Continuous (progressive): Ongoing actions.
- Perfect: Completed actions.
- Perfect Continuous: Actions that have been ongoing for a period.
| Tense Type | Simple | Continuous | Perfect | Perfect Continuous |
| Present | Present Simple | Present Continuous | Present Perfect | Present Perfect Continuous |
| Past | Past Simple | Past Continuous | Past Perfect | Past Perfect Continuous |
| Future | Future Simple | Future Continuous | Future Perfect | Future Perfect Continuous |
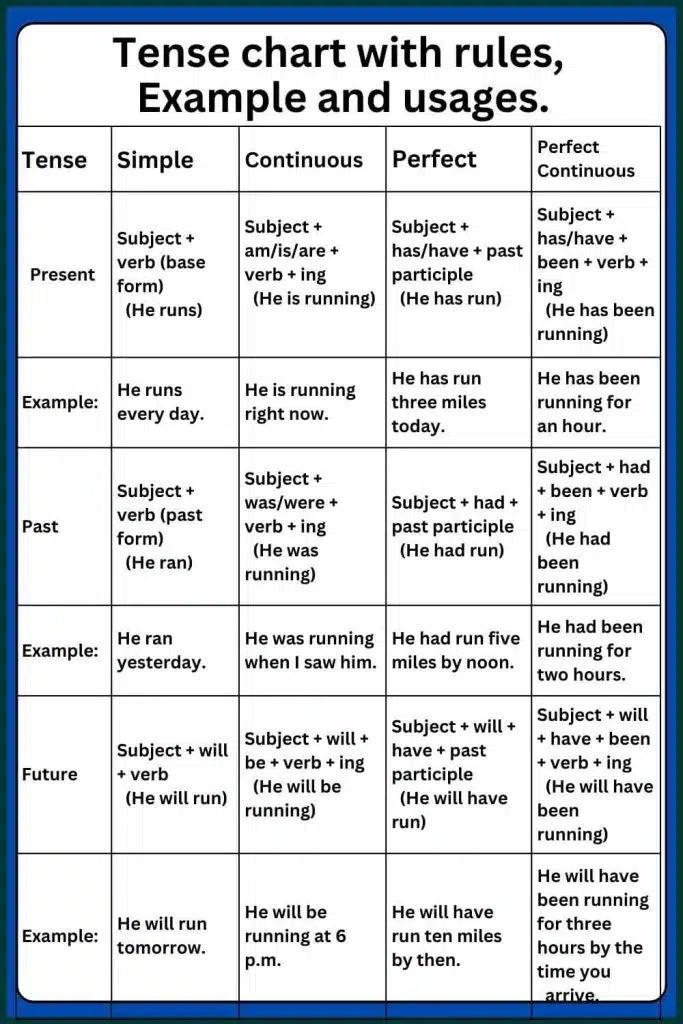
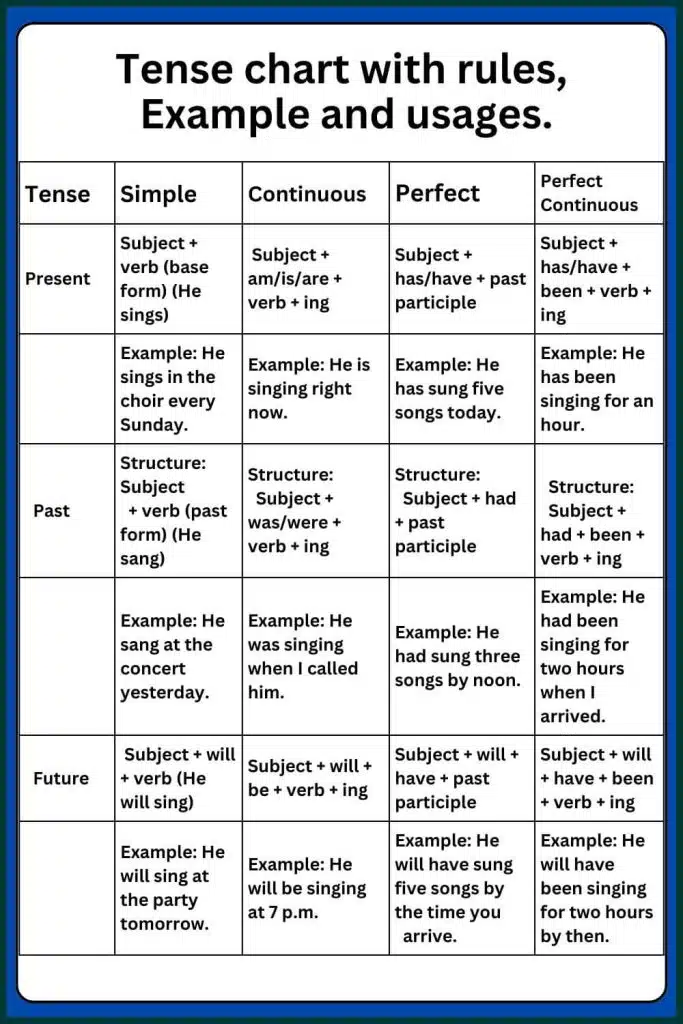
Tense Chart With Rules And Examples
1. Present Simple
- Usage: Expresses habits, general facts, and truths.
- Structure: Subject + base verb (add “s” or “es” for third person singular)
- Example:
- He eats breakfast every day.
- The Earth revolves around the sun.
2. Present Continuous
- Usage: Describes actions happening now or temporary situations.
- Structure: Subject + am/is/are + verb + ing
- Example:
- She is reading a book right now.
- They are watching a movie.
3. Present Perfect
- Usage: Describes actions that happened at an unspecified time or actions with present relevance.
- Structure: Subject + has/have + past participle
- Example:
- I have visited France twice.
- He has completed his homework.
4. Present Perfect Continuous
- Usage: Describes actions that started in the past and are still continuing or have recently stopped.
- Structure: Subject + has/have + been + verb + ing
- Example:
- They have been working on the project for three hours.
- She has been studying all day.
5. Past Simple
- Usage: describes completed actions in the past.
- Structure: Subject + past form of the verb
- Example:
- We went to the park yesterday.
- She called him last night.
6. Past Continuous
- Usage: describes actions that were ongoing at a specific time in the past.
- Structure: Subject + was/were + verb + ing
- Example:
- He was sleeping when the phone rang.
- They were playing soccer at 3 p.m. yesterday.
7. Past Perfect
- Usage: describes actions completed before another action in the past.
- Structure: Subject + had + past participle
- Example:
- She had eaten dinner before he arrived.
- By the time the movie started, they had left.
8. Past Perfect Continuous
- Usage: describes actions that were ongoing before another action in the past.
- Structure: Subject + had + been + verb + ing
- Example:
- He had been working for five hours when they called.
- They had been studying all night before the exam.
9. Future Simple
- Usage: describes actions that will happen in the future.
- Structure: Subject + will + base form of the verb
- Example:
- She will travel to Japan next month.
- They will meet at the restaurant.
10. Future Continuous
- Usage: describes actions that will be ongoing at a specific time in the future.
- Structure: Subject + will + be + verb + ing
- Example:
- He will be working at 5 p.m. tomorrow.
- They will be studying when you arrive.
11. Future Perfect
- Usage: describes actions that will be completed before a certain point in the future.
- Structure: Subject + will + have + past participle
- Example:
- By next week, I will have finished the project.
- They will have arrived before dinner.
12. Future Perfect Continuous
- Usage: describes actions that will have been ongoing for a period of time before a specific future moment.
- Structure: Subject + will + have + been + verb + ing
- Example:
- By the end of this year, he will have been working here for ten years.
- She will have been studying for three hours by the time you arrive.
Common Mistakes When Using Tenses
- Confusing Past Simple and Present Perfect:
- Incorrect: I visited Paris last year.
- Correct: I visited Paris last year.
- Using Future Tense After “If” in Conditional Sentences:
- Incorrect: If it will rain, we will cancel the trip.
- Correct: If it rains, we will cancel the trip.
- Mixing up Continuous and Perfect Tenses:
- Incorrect: She was working there since 2010.
- Correct: She has been working there since 2010.
Tense Chart Overview
| Tense | Example Sentence |
| Present Simple | She writes emails every day. |
| Present Continuous | She is writing an email right now. |
| Present Perfect | She has written three emails today. |
| Present Perfect Continuous | She has been writing emails for the past hour. |
| Past Simple | She wrote an email yesterday. |
| Past Continuous | She was writing an email when I called. |
| Past Perfect | She had written the email before the meeting. |
| Past Perfect Continuous | She had been writing emails before the power went out. |
| Future Simple | She will write an email tomorrow. |
| Future Continuous | She will be writing an email at 3 p.m. |
| Future Perfect | She will have written the email by the time you arrive. |
| Future Perfect Continuous | She will have been writing emails for three hours by 4 p.m. |