When learning English, regular verbs are some of the first you’ll encounter. They are essential to your foundation in the language, as they follow predictable rules for conjugation. This article will explain what regular verbs are, how they work, and how to use them correctly in different tenses. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a clearer understanding of how to conjugate Regular Verbs in English, recognize their patterns, and apply them in your writing and speech.
What Are Regular Verbs in English?
A regular verb is a verb that follows a set pattern when changing to the past tense and past participle forms. In English, these verbs form their simple past and past participle by adding “-ed” to the base form (or “-d” if the verb ends in “e”). These verbs are predictable, which makes them easier to learn compared to irregular verbs, which have varied forms.
For example:
Talk → talked → talked
Jump → jumped → jumped
Regular verbs are important because they are the most common type of verb in English. Most verbs you will use in daily communication are regular, so understanding them will significantly improve your speaking and writing skills.
How to Conjugate Regular Verbs in English
Conjugating regular verbs in English involves changing the base form of the verb to match the appropriate tense. While the process for most regular verbs is straightforward, there are a few variations to keep in mind. Here’s a guide to help you:
1. For Most Regular Verbs
To form the past tense and past participle, simply add “-ed” to the base verb. This rule works for most regular verbs.
Examples:
Call → called → called
Dance → danced → danced
2. For Verbs Ending in “-e”
If a verb already ends in “-e,” simply add “-d” to form the past tense and past participle.
Examples:
Live → lived → lived
Dance → danced → danced
3. For Verbs Ending in Consonant + Vowel + Consonant
If a verb ends in a consonant-vowel-consonant (CVC) pattern, double the final consonant before adding “-ed.”
Examples:
Hop → hopped → hopped
Stop → stopped → stopped
4. For Verbs Ending in “-y”
If the verb ends in a consonant + “-y,” drop the “y” and add “-ied.”
Examples:
Cry → cried → cried
Carry → carried → carried
5. For Verbs with Other Endings
For most other verbs, simply add “-ed” without any changes to the ending.
Examples:
Start → started → started
Jump → jumped → jumped
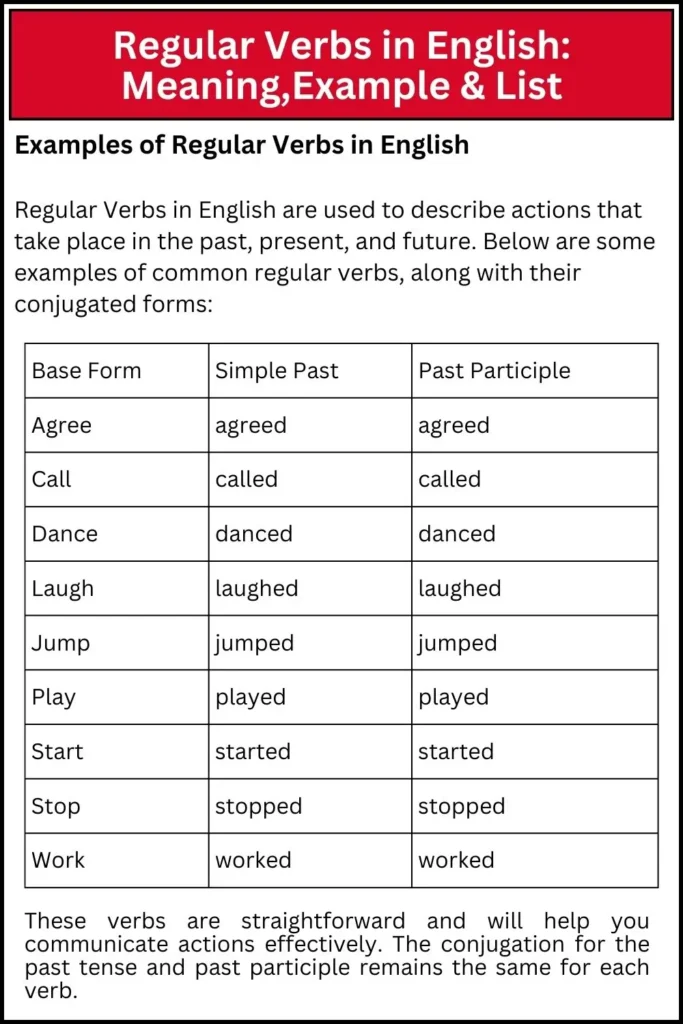
Examples of Regular Verbs in English
Regular Verbs in English are used to describe actions that take place in the past, present, and future. Below are some examples of common regular verbs, along with their conjugated forms:
| Base Form | Simple Past | Past Participle |
|---|---|---|
| Agree | agreed | agreed |
| Call | called | called |
| Dance | danced | danced |
| Laugh | laughed | laughed |
| Jump | jumped | jumped |
| Play | played | played |
| Start | started | started |
| Stop | stopped | stopped |
| Work | worked | worked |
These verbs are straightforward and will help you communicate actions effectively. The conjugation for the past tense and past participle remains the same for each verb.
Regular Verbs vs. Irregular Verbs
While Regular Verbs in English follow clear rules for conjugation, irregular verbs do not. Irregular verbs change in various unpredictable ways when they form the past tense and past participle. For example:
Go → went → gone (irregular)
Eat → ate → eaten (irregular)
Regular Verbs in English are much easier to learn since they follow a set pattern, while irregular verbs require more memorization. However, both types of verbs are essential for mastering English.
Examples of Regular and Irregular Verbs:
| Regular Verb | Irregular Verb |
|---|---|
| Talk → talked → talked | Go → went → gone |
| Play → played → played | Eat → ate → eaten |
| Laugh → laughed → laughed | See → saw → seen |
Tips for Mastering Regular Verbs in English
Practice Regularly: The best way to master regular verbs is through practice. Conjugate verbs in different tenses and use them in sentences to reinforce their patterns.
Focus on Common Verbs: Start by learning the most common regular verbs. This will give you a solid foundation for speaking and writing in English.
Use Flashcards: Create flashcards to test your knowledge of regular verbs and their forms. This will help reinforce the conjugation rules.
Write Sentences: Write sentences using regular verbs in various tenses. For example, write about what you did yesterday, what you’re doing today, and what you will do tomorrow.
Listen to Native Speakers: Pay attention to how native speakers use regular verbs in context. This will help you internalize their usage and pronunciation.
How to Use Regular Verbs in Sentences
Now that you understand the basics of conjugating Regular Verbs in English, let’s explore how to use them in sentences. Understanding how to apply regular verbs in context is key to communicating effectively in English. Regular verbs are used in both formal and informal settings, in conversations, writing, and storytelling.
1. Using Regular Verbs in the Simple Past Tense
The simple past tense describes actions that were completed in the past. To form this tense with regular verbs, simply add “-ed” to the base form.
Examples:
I talked to my friend yesterday.
She played tennis last weekend.
We watched a movie last night.
In all these sentences, the actions (talk, play, watch) happened in the past, and the simple past tense is used to describe them.
2. Using Regular Verbs in the Past Participle Form
The past participle is often used in perfect tenses (like the present perfect, past perfect, etc.) and the passive voice. The past participle of regular verbs is identical to the simple past form (both end in “-ed”).
Examples:
I have studied all day. (Present perfect tense)
The letter was mailed yesterday. (Passive voice)
She had already finished her homework when I called. (Past perfect tense)
In these examples, the past participle form of the regular verb is used to describe actions that are either completed before the present time or happened in the past.
3. Using Regular Verbs in the Future Tense
In the future tense, regular verbs retain their base form, and “will” or “shall” is used before the verb.
Examples:
I will call you tomorrow.
They will start the project next week.
We will visit the museum soon.
In these examples, the base form of the regular verb is used after the auxiliary verb “will” to talk about actions that will happen in the future.
4. Using Regular Verbs as Adjectives
In addition to being used in tenses, regular verbs can also function as adjectives. This happens when the verb is in its past participle form, often describing something that has already happened.
Examples:
The broken window needs to be fixed. (Describes a window that was broken)
I have a completed report. (Describes a report that is finished)
He wore a damaged coat. (Describes a coat that is damaged)
In these sentences, the past participles “broken,” “completed,” and “damaged” describe the nouns that they modify.
Common Mistakes with Regular Verbs in English
Even though regular verbs are easier to conjugate than irregular verbs, there are still some common mistakes learners make when using them. Being aware of these mistakes will help you avoid them.
1. Adding “-ed” to Irregular Verbs
Sometimes learners mistakenly add “-ed” to irregular verbs, like go, thinking that all verbs follow the same conjugation rules. However, irregular verbs do not follow the regular “-ed” pattern.
Incorrect: I goed to the store. Correct: I went to the store.
2. Doubling the Final Consonant Incorrectly
When Regular Verbs in English end in a consonant-vowel-consonant pattern, you should double the final consonant before adding “-ed.” However, do not double the consonant if the final syllable is not stressed.
Incorrect: She stopped by the store. (Correct, because “stop” is stressed) Correct: He cancelled the meeting. (Incorrect, because the final syllable of “cancel” is not stressed)
3. Misusing the “-y” Ending
For regular verbs that end in “-y,” you need to drop the “y” and add “-ied” to form the past tense and past participle. However, if the verb ends in a vowel + “y,” you simply add “-ed.”
Incorrect: He played yesterday. (Correct) Correct: She cryed after the movie. (Incorrect; it should be “cried”)
4. Confusing Regular and Irregular Forms
Some verbs can have both regular and irregular forms. For example, learned is the regular past tense, but learnt is the irregular form commonly used in British English.
Example:
American English: I learned about it yesterday.
British English: I learnt about it yesterday.
Regular Verbs in Different Forms of Communication
Regular Verbs in English are not only used in everyday speech, but they also play an important role in both written and formal communication. Let’s explore how they are used across different forms of communication:
1. In Written English
In writing, Regular Verbs in English are used in stories, essays, emails, and reports. Whether you’re narrating a story or providing a summary of events, regular verbs help provide structure to your writing.
Example (Story):
Yesterday, I watched a great movie. It told the story of a young girl who found her way back home after being lost for years.
2. In Formal Writing
Regular Verbs in English are essential in formal writing, like academic papers, business reports, or professional emails. They maintain clarity and keep sentences easy to read.
Example (Business email):
I appreciated your prompt response to my inquiry.
We received your application and will contact you soon.
3. In Informal Communication
In casual conversations or informal writing (texts, social media, etc.), regular verbs still play a key role. They help convey actions and events clearly without any confusion.
Example (Text message):
I finished the assignment. Let’s go out for lunch now.
Conclusion On Regular Verbs in English
Regular Verbs in English are an essential part of English grammar. They follow predictable patterns for conjugation, making them easier to learn and use. By practicing and understanding these rules, you can improve your fluency and accuracy in speaking and writing English. Keep learning and practicing regular verbs, and soon, you’ll be able to conjugate them effortlessly in various tenses. Stay consistent, and you’ll see the results in no time.

