Understanding the present perfect tense is vital in English. It’s used to link the past with the present.
The present perfect tense often confuses learners. It combines the present moment with past actions. This tense shows that something happened at an unspecified time before now. It can also indicate an action that started in the past and continues in the present.
Mastering this tense will improve your English skills. In this blog post, you will find clear examples. These examples will help you see how the present perfect tense works. Let’s dive in and explore the present perfect tense structure with examples that will enhance your understanding and usage.
Introduction to Present Perfect Tense
The Present Perfect Tense is a crucial aspect of English grammar. It connects the past with the present. This tense helps in expressing actions that happened at an unspecified time. It also shows actions that started in the past and continue to the present.
What Is Present Perfect Tense?
The Present Perfect Tense uses the auxiliary verb “have/has” and the past participle of the main verb. For example:
- She has finished her homework.
- They have traveled to many countries.
This tense is used to describe:
- Actions that happened at an unspecified time in the past.
- Actions that started in the past and still continue.
- Recent actions that have relevance to the present.
Importance In English
Understanding the Present Perfect Tense is essential for mastering English. It helps in:
- Describing experiences: “I have seen that movie.”
- Talking about changes over time: “He has become more responsible.”
- Discussing accomplishments: “They have completed the project.”
Using this tense correctly can make your English sound more natural. It also helps in making your conversations more precise and clear.
Forming The Present Perfect Tense
The present perfect tense is a vital aspect of English grammar. It connects past actions to the present. Understanding how to form this tense can improve your English significantly.
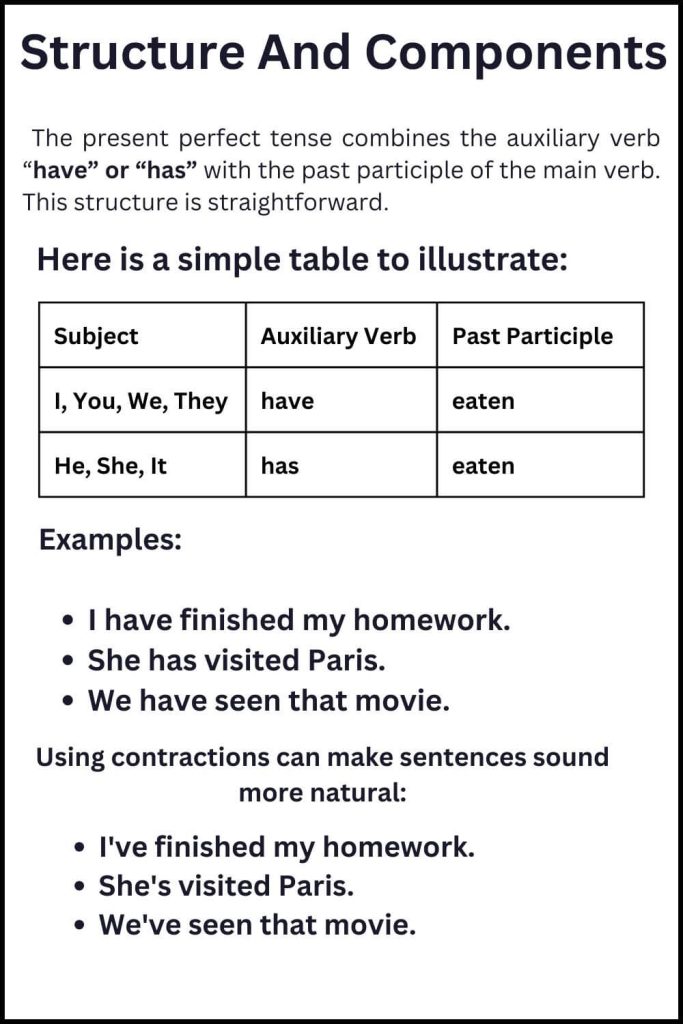
Structure And Components
The present perfect tense combines the auxiliary verb “have” or “has” with the past participle of the main verb. This structure is straightforward.
Here is a simple table to illustrate:
| Subject | Auxiliary Verb | Past Participle |
| I, You, We, They | have | eaten |
| He, She, It | has | eaten |
Examples:
- I have finished my homework.
- She has visited Paris.
- We have seen that movie.
Using contractions can make sentences sound more natural:
- I’ve finished my homework.
- She’s visited Paris.
- We’ve seen that movie.
Common Mistakes
There are some common mistakes learners make with the present perfect tense. Here are some to watch out for:
- Using the wrong auxiliary verb. Remember, use “have” for plural subjects and “has” for singular subjects.
- Incorrect past participle form. Some verbs have irregular past participles. For example, “go” becomes “gone”, not “goed”.
- Confusing present perfect with past simple. The present perfect connects past actions to the present. Past simple is used for actions that happened and finished in the past.
Examples:
- Incorrect: I have went to the store.
- Correct: I have gone to the store.
By understanding the structure and common mistakes, you can use the present perfect tense correctly and effectively.
Positive Sentences
The present perfect tense helps us talk about actions that happened at an unspecified time. We often use it to show that an action has relevance to the present.
Positive sentences in this tense are straightforward. They use the structure: subject + have/has + past participle.
Basic Examples
Below are some simple examples of positive sentences in the present perfect tense:
- I have eaten breakfast today.
- She has visited Paris three times.
- They have finished their homework.
Notice the use of ‘have’ with plural subjects and ‘has’ with singular subjects.
Advanced Examples
Advanced examples show how the present perfect tense can convey more complex ideas:
- We have been friends for ten years.
- She has lived in three different countries.
- They have worked on this project since last year.
These sentences often include time expressions like ‘for’ and ‘since’ to indicate duration.
Negative Sentences
The present perfect tense is essential for expressing actions that have occurred at an unspecified time before now. In this section, we will focus on negative sentences in the present perfect tense. Negative sentences tell us that something did not happen. Understanding these sentences helps in improving your English proficiency.
Basic Examples
Let’s start with some basic examples of negative sentences in the present perfect tense:
- I have not finished my homework.
- She has not eaten breakfast yet.
- They have not visited the museum.
- We have not seen that movie.
- He has not called his friend.
In these sentences, “have not” or “has not” is used with the past participle of the verb. This structure clearly indicates that the action did not happen.
Advanced Examples
Now, let’s look at some advanced examples to understand negative sentences better:
- She hasn’t traveled abroad since last year.
- They haven’t completed the project despite working hard.
- We haven’t seen each other for a long time.
- He hasn’t spoken to his neighbor since the argument.
- I haven’t received any emails today.
Notice how these sentences use contractions like “hasn’t” and “haven’t.” The use of time expressions like “since,” “for,” and “today” adds context.
Questions In Present Perfect
Understanding how to ask questions in the present perfect tense is crucial. This tense connects past actions with the present. It helps in showing the result of an action or its relevance to the present moment. In this section, we will explore how to form questions in the present perfect tense and provide examples to illustrate their use.
How to Form Questions
Forming questions in the present perfect tense is straightforward. It involves the following structure:
| Structure | Explanation |
| Have/Has + Subject + Past Participle + ? | The question starts with “have” or “has”, followed by the subject and the past participle of the verb. |
Use “have” for plural subjects and “has” for singular subjects.
Examples of Questions
Here are some examples to help you understand better:
- Have you finished your homework?
- Has she visited the new museum?
- Have they read the book?
- Has it rained today?
- Have we met before?
Notice the structure in each example:
- Start with “have” or “has”.
- Add the subject (you, she, they, it, we).
- Include the past participle of the main verb (finished, visited, read, rained, met).
These examples show how to form questions in the present perfect tense. Practice using this structure to improve your English skills.
Present Perfect Vs. Past Simple
Understanding the difference between the Present Perfect and Past Simple tenses can be tricky. Both tenses talk about actions that happened in the past. But they are used in different ways. This section will help you understand when to use each tense.
Key Differences
The Present Perfect tense connects the past with the present. It often shows actions that started in the past but are still relevant now.
The Past Simple tense describes actions that happened at a specific time in the past. These actions are finished and have no connection to the present.
| Present Perfect | Past Simple |
| Uses ‘has/have’ + past participle | Uses past verb forms |
| “I have eaten breakfast.” | “I ate breakfast yesterday.” |
Usage Scenarios
- Present Perfect: Use for actions that have an effect on the present.
- Example: “She has lost her keys.” (She still doesn’t have them)
- Past Simple: Use for actions that happened at a specific time in the past.
- Example: “She lost her keys yesterday.”

Here are some more examples:
- Present Perfect: “We have visited Paris several times.”
- Past Simple: “We visited Paris in 2010.”
- Present Perfect: “They have finished their homework.”
- Past Simple: “They finished their homework before dinner.”
Remember, the Present Perfect often uses words like already, just, and yet. The Past Simple often uses words like yesterday, last week, and in 2010.
Common Expressions
The present perfect tense is commonly used in English. It helps to connect the past with the present. In this section, we will explore some common expressions used with the present perfect tense.
Frequently Used Phrases
Here are some phrases often used with the present perfect tense. These phrases help convey the sense of time and action.
- Already – to indicate something happened sooner than expected.
- Yet – used in negative sentences and questions to show something has not happened up to now.
- Just – to show something happened very recently.
- Ever – used in questions to ask if something has happened at any time.
- Never – to show that something has not happened at any time.
- So far – to indicate something has happened up to the present moment.
- Recently – to show that something happened a short time ago.
Examples In Context
Let’s see these phrases in action with examples. Each example uses the present perfect tense to show how these phrases function in sentences.
| Phrase | Example Sentence |
| Already | She has already finished her homework. |
| Yet | Has he called you yet? |
| Just | I have just eaten lunch. |
| Ever | Have you ever been to Paris? |
| Never | I have never seen that movie. |
| So far | We have completed three projects so far. |
| Recently | They have recently moved to a new house. |
Practical Exercises
The present perfect tense can be a bit tricky. But don’t worry! With practical exercises, you can master it. Here are some exercises that will help you understand and use the present perfect tense correctly.
Fill-in-the-blanks
Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verb in parentheses. This will help you practice the present perfect tense.
- I ______ (finish) my homework.
- She ______ (visit) Paris three times.
- They ______ (not/see) that movie yet.
- We ______ (live) here since 2015.
- He ______ (work) at this company for ten years.

Sentence Rewriting
Rewrite the sentences below in the present perfect tense. This will help you understand how to form sentences using the present perfect tense.
- She goes to the store. (has gone)
- They eat breakfast. (have eaten)
- I read that book. (have read)
- He writes a letter. (has written)
- We take a trip to Spain. (have taken)
By practicing these exercises, you’ll get better at using the present perfect tense. Remember, practice makes perfect!
FAQ- Present perfect tense structure with examples
What Is The Present Perfect Tense?
The present perfect tense connects past actions with the present. It uses “has” or “have” plus the past participle of the verb.
How Is The Present Perfect Tense Formed?
The present perfect tense is formed using “has” or “have” followed by the past participle of the verb.
When Do We Use The Present Perfect Tense?
We use the present perfect tense for actions that happened at an unspecified time or started in the past and continue now.
Can You Give Examples Of Present Perfect Tense?
Sure! Examples: “She has visited Paris. ” “They have finished their homework. ” “I have known him for years. “

