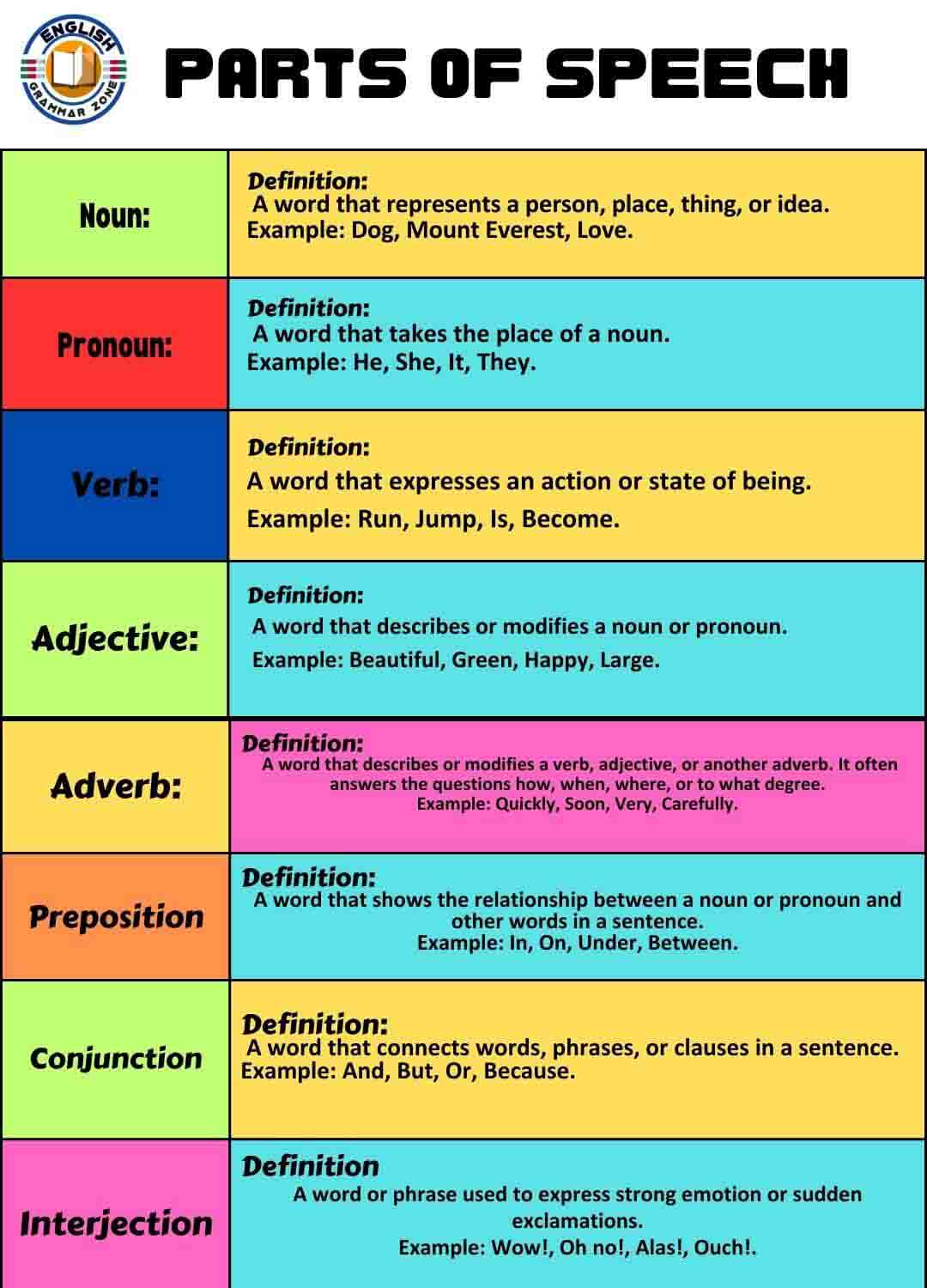
Parts of speech with types and examples are the fundamental building blocks of language, and they are categorized based on the roles they play in a sentence. Here are the main parts of speech along with their definitions and examples:
Parts of Speech with Types and Examples
Language is a complex system that allows us to communicate thoughts, ideas, and emotions. At the foundation of this communication are parts of speech, which are the building blocks of sentences. knowing the parts of speech is important for mastering a language, whether for writing, speaking, or understanding others. This article will delve into the eight main parts of speech, their types, and give examples to illustrate their use in sentences.
1. Nouns
Definition: A noun is a word that represents a person, place, thing, or idea. Nouns can be classified into several types:
Types of Nouns:
Common Nouns: General names of people or things (e.g., dog, city, book).
Proper Nouns: Specific names of people or places, always capitalized (e.g., John, Paris, Monday).
Abstract Nouns: Names for things that are not tangible (e.g., love, bravery, happiness).
Concrete Nouns: Names for things that can be perceived through the senses (e.g., apple, car, music).
Collective Nouns: Names for a group of people or things (e.g., team, flock, bunch).
Examples:
Common Noun: The cat sat on the table.
Proper Noun: Emily went to New York last summer.
Abstract Noun: His happiness was contagious.
Concrete Noun: The coffee was hot and fragrant.
Collective Noun: The team celebrated their victory.
2. Pronouns
Definition: A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun to avoid repetition. Pronouns can represent people, objects, or things.
Types of Pronouns:
Personal Pronouns : Refer to specific persons or things (e.g., I, you, he, she, it, we, they).
Possessive Pronouns : Indicate ownership (e.g., mine, yours, his, hers, ours, theirs).
Reflexive Pronouns : Refer back to the subject of the sentence (e.g., myself, yourself, himself, herself).
Relative Pronouns : Introduce relative clauses (e.g., who, whom, whose, which, that).
Demonstrative Pronouns : Point to specific things (e.g., this, that, these, those).
Indefinite Pronouns : Refer to non-specific persons or things (e.g., someone, anyone, everyone, something, anything).
Examples:
Personal Pronoun: She loves to read books.
Possessive Pronoun: That book is mine.
Reflexive Pronoun: He made the cake himself.
Relative Pronoun: The girl who won the contest is my sister.
Demonstrative Pronoun: This is my favorite jacket.
Indefinite Pronoun: Everyone enjoyed the party.
3. Verbs
Definition: A verb is a word that expresses action, occurrence, or state of being. Verbs are vital as they indicate what the subject does or what happens to the subject.
Types of Verbs:
Action Verbs: Describe physical or mental actions (e.g., run, think, eat).
Linking Verbs : Connect the subject to a subject complement (e.g., be, become, seem).
Auxiliary (Helping) Verbs : Assist the main verb in a sentence (e.g., is, are, have, will).
Transitive Verbs : Require a direct object to complete their meaning (e.g., She kicked the **ball**).
Intransitive Verbs : Do not require a direct object (e.g., He sleeps).
Examples:
Action Verb: The dog barks loudly.
Linking Verb: She is a talented musician.
Auxiliary Verb: They have finished their homework.
Transitive Verb: The teacher reads a book to the class.
Intransitive Verb: He sneezed unexpectedly.
4. Adjectives
Definition : An adjective is a word that describes or modifies a noun or pronoun, providing more information about its characteristics.
Types of Adjectives:
Descriptive Adjectives: Describe qualities or features (e.g., beautiful, tall, interesting).
Quantitative Adjectives: Indicate quantity (e.g., some, many, few).
Demonstrative Adjectives : Point to specific nouns (e.g., this, that, these, those).
Possessive Adjectives: Show ownership (e.g., my, your, his, her).
Interrogative Adjectives: Used to ask questions (e.g., which, what, whose).
Examples:
Descriptive Adjective: The colorful painting caught my attention.
Quantitative Adjective: She has three dogs.
Demonstrative Adjective: This book is mine.
Possessive Adjective: Her car is parked outside.
Interrogative Adjective: Which route should we take?
5. Adverbs
Definition: An adverb is a word that modifies a verb, adjective, or another adverb, often indicating manner, place, time, frequency, or degree.
Types of Adverbs:
Adverbs of Manner: Describe how an action is performed (e.g., quickly, slowly, carefully).
Adverbs of Time: Indicate when an action occurs (e.g., now, later, yesterday).
Adverbs of Place : Describe where an action occurs (e.g., here, there, everywhere).
Adverbs of Frequency: Indicate how often an action occurs (e.g., always, often, seldom).
Adverbs of Degree : Describe the intensity or degree of an adjective or another adverb (e.g., very, quite, too).
Examples:
Adverb of Manner: She danced gracefully at the recital.
Adverb of Time: We will meet tomorrow .
Adverb of Place: The cat is hiding under the table.
Adverb of Frequency: He usually wakes up early.
Adverb of Degree: This task is very challenging.
6. Prepositions
Definition: A preposition is a word that shows the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence, indicating direction, place, time, or manner.
Types of Prepositions:
Prepositions of Time: Indicate when something happens (e.g., at, on, in).
Prepositions of Place: Indicate where something is (e.g., under, above, between).
Prepositions of Direction: Indicate movement toward something (e.g., to, into, through).
Prepositions of Manner: Describe how something is done (e.g., by, with).
Examples:
Preposition of Time: The meeting is at 3 PM.
Preposition of Place: The book is on the shelf.
Preposition of Direction: She walked to the park.
Preposition of Manner: He solved the problem with ease.
7. Conjunctions
Definition: A conjunction is a word that connects words, phrases, or clauses, helping to build complex and coherent sentences.
Types of Conjunctions:
Coordinating Conjunctions: Connect words, phrases, or clauses of equal importance (e.g., and, but, or, nor, for, so, yet).
Subordinating Conjunctions: Connect a dependent clause to an independent clause (e.g., because, although, since, while).
Correlative Conjunctions: Work in pairs to connect equal elements (e.g., either…or, neither…nor, not only…but also).
Examples:
Coordinating Conjunction: I wanted to go for a walk, but it started to rain.
Subordinating Conjunction: Although it was cold, we decided to go hiking.
Correlative Conjunction: Either you can join us for dinner, or you can stay home.
8. Interjections
Definition: An interjection is a word or phrase that expresses strong emotion or surprise. Interjections are often standalone and can convey feelings like excitement, joy, or frustration.
Examples:
Wow! That was an incredible performance!
Oh no! I forgot my wallet at home.
Hooray! We won the game!
Conclusion
Understanding the parts of speech with types and examples is crucial for effective communication in any language. Each part of speech plays an individual role in sentence structure, providing clarity and meaning to our expressions. By familiarizing ourselves with the types of parts of speech and their examples, we can enhance our writing and speaking skills, making our communication more impactful and engaging.
Part of Speech