Understanding basic financial vocabulary is essential for anyone stepping into the world of business. In this blog post, we’ll explore key business English financial terms that are commonly used in meetings, reports, and everyday professional conversations. Whether you’re a student, a new employee, or just starting your journey in business English, this guide will help you learn the meaning of important terms like profit, revenue, assets, and more — all in simple, beginner-friendly language.
Business English Financial Terms
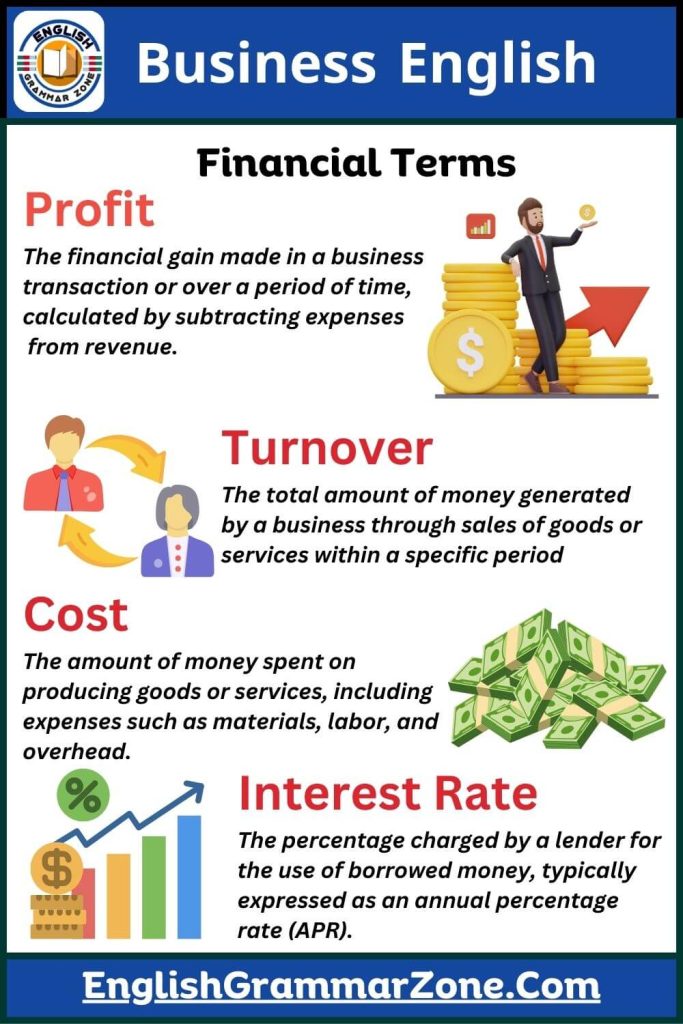
Profit
The financial gain made in a business transaction or over a period of time, calculated by subtracting expenses from revenue.
Turnover
The total amount of money generated by a business through sales of goods or services within a specific period.
Cost
The amount of money spent on producing goods or services, including expenses such as materials, labor, and overhead.
Interest Rate
The percentage charged by a lender for the use of borrowed money, typically expressed as an annual percentage rate (APR).
Asset
Something owned by a person or company that has value and can be used or sold to pay debts.
Liability
A financial obligation or debt owed by a person or company, typically arising from past transactions or events.
Detailed explanations of business English financial terms:
- Profit: Profit is the financial gain realized from a business transaction or over a period of time. It is calculated by subtracting all expenses, including operating costs, taxes, and interest, from total revenue or income generated by the business. Profit is a crucial indicator of a business’s financial health and success. There are different types of profit, such as gross profit (revenue minus cost of goods sold) and net profit (total revenue minus total expenses).
- Turnover: Turnover refers to the total amount of money generated by a business through the sales of goods or services within a specific period, typically annually. It represents the business’s ability to generate income from its core operations. Turnover is also known as revenue or sales and is a key metric in assessing the size and activity level of a business. It excludes any taxes or expenses associated with generating that revenue.
- Cost: Cost refers to the amount of money expended on producing goods or services. It encompasses various expenses incurred during the production process, including raw materials, labor wages, utilities, rent for facilities, and other overhead costs. Understanding and managing costs is essential for businesses to maintain profitability and efficiency. Costs can be categorized into fixed costs (such as rent and salaries) and variable costs (such as raw materials and utilities), depending on whether they fluctuate with production levels.
- Interest Rate: Interest rate is the percentage charged by a lender for the use of borrowed money, usually expressed as an annual percentage rate (APR). It is a key component in finance, influencing borrowing costs and returns on savings or investments. Interest rates vary depending on factors such as inflation, economic conditions, risk associated with the borrower, and the duration of the loan or investment. Higher interest rates generally indicate higher risk or inflation expectations.
- Asset: An asset is anything of value owned by a person or entity that can be converted into cash. Assets are typically categorized into current assets (e.g., cash, accounts receivable) and non-current assets (e.g., property, equipment, long-term investments). They represent economic resources that provide future benefits to the owner, such as generating revenue or reducing future expenses. Assets are recorded on a company’s balance sheet and are essential for assessing its financial position and performance.
- Liability: A liability is a financial obligation or debt owed by an individual or entity arising from past transactions or events. It represents an obligation to transfer economic benefits (usually cash) to another party in the future. Liabilities can include accounts payable, loans, mortgages, accrued expenses, and other financial obligations. They are recorded on the balance sheet as either current liabilities (due within one year) or non-current liabilities (due after one year). Managing liabilities is crucial for maintaining financial stability and liquidity.
Read More

