Learning to communicate effectively in English requires a strong understanding of grammar, and one crucial area is mastering past tenses. Past tenses help us talk about events, experiences, and actions that have already occurred. From describing a memorable vacation to narrating historical events, past tenses make our stories come alive. However, many learners find it challenging to differentiate between the various forms of past tenses and use them correctly. This guide will simplify the rules, explain the differences, and provide helpful examples to make mastering past tenses easier than ever.
Past Tense Structure with Example
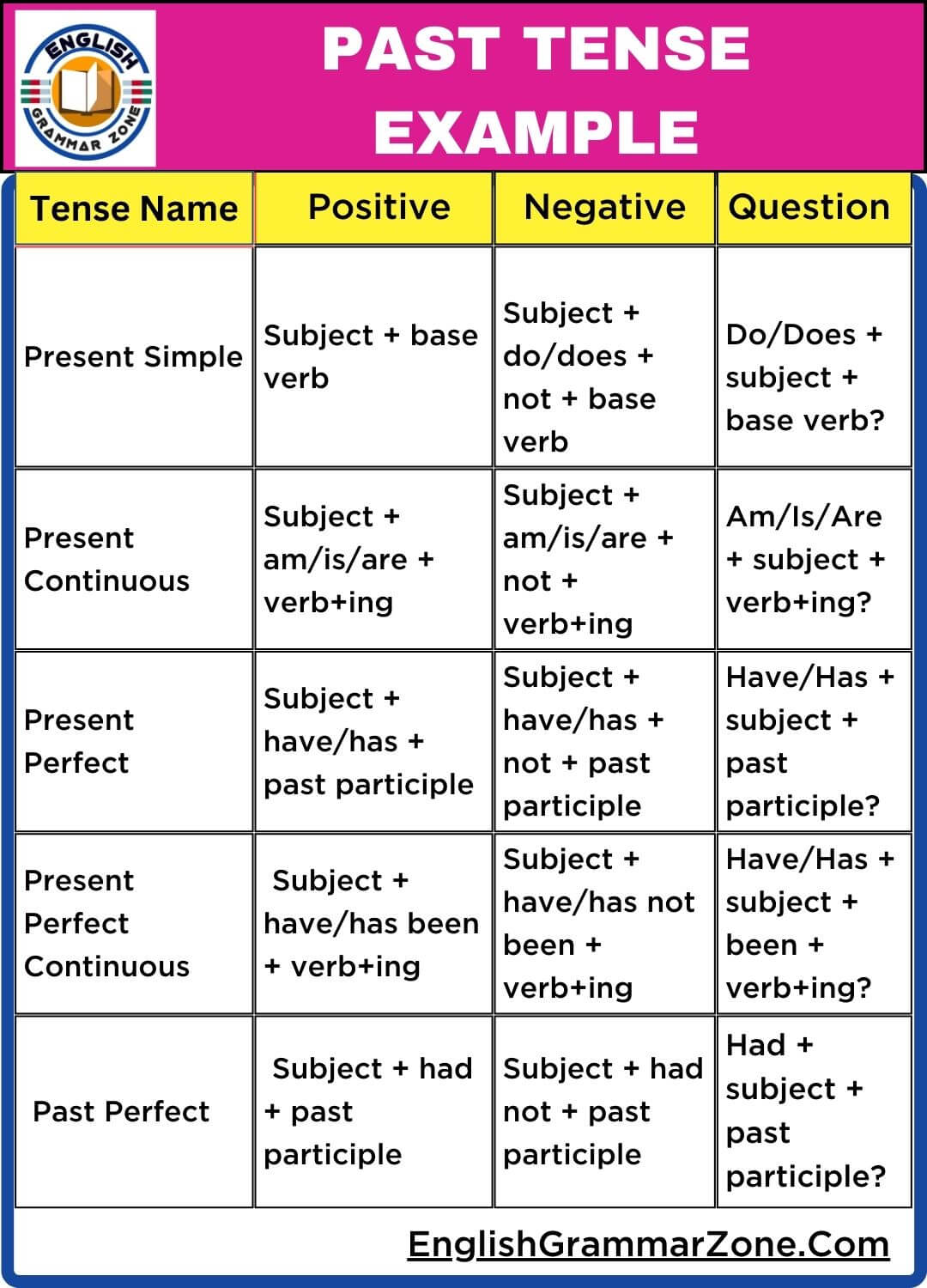
| Tense Name | Positive | Negative | Question |
| Past Simple | Subject + past verb | Subject + did not + base verb | Did + subject + base verb? |
| She walked to school. | She did not walk to school. | Did she walk to school? | |
| Past Continuous | Subject + was/were + verb+ing | Subject + was/were not + verb+ing | Was/Were + subject + verb+ing? |
| I was reading a book. | I was not reading a book. | Was I reading a book? | |
| Past Perfect | Subject + had + past participle | Subject + had not + past participle | Had + subject + past participle? |
| They had finished their homework. | They had not finished their homework. | Had they finished their homework? | |
| Past Perfect Continuous | Subject + had been + verb+ing | Subject + had not been + verb+ing | Had + subject + been + verb+ing? |
| She had been studying for two hours. | She had not been studying for two hours. | Had she been studying for two hours? |
Picture: 1
Picture: 2

Frequently Asked Questions About Mastering Past Tenses
1. What Are Past Tenses?
Past tenses are verb forms used to describe actions or events that happened in the past. In English, there are four main types of past tenses:
- Simple Past: Used for completed actions (e.g., “I visited the park.”)
- Past Continuous: Describes ongoing actions in the past (e.g., “I was reading a book.”)
- Past Perfect: Indicates an action that was completed before another past event (e.g., “I had eaten before they arrived.”)
- Past Perfect Continuous: Focuses on actions that were ongoing before another past event (e.g., “I had been working for hours when the meeting started.”)
2. Why Is Mastering Past Tenses Important?
Mastering past tenses is essential for clear communication. Whether you’re writing a story, discussing your past experiences, or explaining historical facts, correct use of past tenses ensures your message is understood. Misusing tenses can confuse your audience and make your communication less effective.
3. What Is the Difference Between Simple Past and Past Perfect?
The Simple Past is used for actions that are finished, with no reference to another event (e.g., “She called me yesterday.”).
The Past Perfect, however, shows that one action occurred before another (e.g., “She had called me before I arrived.”).
A simple way to remember this is: the past perfect tense always involves a sequence of events, while the simple past is more straightforward.
4. How Do I Use Past Continuous Tense Correctly?
The past continuous is used to describe actions that were happening at a specific moment in the past. For example:
- “I was cooking dinner when the phone rang.”
Here, the past continuous (“was cooking”) shows the ongoing action, while the simple past (“rang”) highlights the interrupting event.
This tense is also used to set the scene in storytelling, such as:
- “The sun was setting, and birds were singing.”
5. What Are Common Mistakes in Using Past Tenses?
Some common errors include:
- Mixing Tenses Incorrectly: Using past continuous where simple past is needed (e.g., “I was ate dinner” instead of “I ate dinner”).
- Overusing Past Perfect: Adding “had” unnecessarily (e.g., “I had went to the park” instead of “I went to the park”).
- Omitting Time References: Forgetting to include words like “yesterday,” “last week,” or “two years ago” can make sentences unclear.
6. How Can I Practice and Master Past Tenses?
Here are a few tips:
- Write Daily: Practice writing short paragraphs about your day or past experiences.
- Read Stories: Pay attention to how authors use different past tenses.
- Take Quizzes: Online grammar quizzes can help you test and improve your skills.
- Speak Regularly: Try telling stories or sharing memories in English to build confidence.
Mastering past tenses may seem overwhelming at first, but with consistent practice and attention to detail, you’ll soon find yourself using them naturally.
By understanding the nuances of past tenses and applying them correctly, you’ll be able to communicate your thoughts more clearly and effectively. Keep practicing, and you’ll soon become a pro at mastering past tenses!

