Adverb prepositional phrases are an essential part of English grammar, allowing speakers and writers to add rich detail, clarify meaning, and enhance sentence variety. They modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs by providing information about time, place, manner, reason, and more. Mastering these phrases empowers English learners to communicate with greater precision and fluency.
This comprehensive article offers an accessible yet in-depth exploration of adverb prepositional phrases. You’ll find:
- Clear definitions and explanations
- Step-by-step breakdowns of structure and function
- Over 100 categorized examples with contextualized sentences
- Comparison tables and reference charts
- Usage rules and common pitfalls
- Interactive exercises with answer keys
- Advanced insights and a detailed FAQ
Whether you’re a student aiming to improve your writing, a teacher seeking teaching materials, or a writer looking for stylistic variety, this guide will boost your understanding and usage of adverb prepositional phrases. Let’s dive in!
Table of Contents
- 3. Definition Section
- 4. Structural Breakdown
- 5. Types or Categories of Adverb Prepositional Phrases
- 6. Examples Section (100 Examples)
- 7. Usage Rules
- 8. Common Mistakes
- 9. Practice Exercises
- 10. Advanced Topics
- 11. FAQ Section
- 12. Conclusion
3. DEFINITION SECTION
3.1 What Is a Prepositional Phrase?
A prepositional phrase is a group of words that begins with a preposition and ends with its object (a noun or pronoun), often including modifiers of the object.
Examples:
- in the morning (prep + article + noun)
- under the old wooden bridge (prep + modifiers + noun)
- between us (prep + pronoun)
3.2 What Is an Adverb Prepositional Phrase?
An adverb prepositional phrase is a prepositional phrase that functions as an adverbial modifier. It modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb by answering questions like when?, where?, how?, why?, under what condition?, or to what extent?
Examples:
- She ran through the park. (modifies verb ran; tells where)
- He is good at singing. (modifies adjective good; tells in what)
- She spoke with great enthusiasm. (modifies verb spoke; tells how)
They provide essential details that enrich communication.
3.3 Grammatical Classification
Within sentence structure, adverb prepositional phrases act as adverbials. They differ from adjective prepositional phrases, which modify nouns or pronouns.
Adverbial PP: He arrived on time. (modifies verb)
Adjectival PP: The book on the table is mine. (modifies noun book)
3.4 Functions & Usage Contexts
They frequently:
- Modify verbs: He laughed with joy.
- Modify adjectives: She’s proud of her achievements.
- Modify adverbs: He completed the task in record time.
| Function | Modifies | Example | Question Answered |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adjective PP | Noun | The man with the hat | Which man? |
| Adverb PP | Verb/Adj/Adv | He ran with speed | How did he run? |
4. STRUCTURAL BREAKDOWN
4.1 Components of a Prepositional Phrase
The typical structure is:
Preposition + Object (noun/pronoun) + Modifiers
Example:
- on (prep) a cold winter morning (object + adj modifiers)
- by (prep) herself (pronoun object)
4.2 Position in a Sentence
Adverb prepositional phrases can occur in three main positions:
- Initial (beginning): In the morning, she jogs. (adds emphasis or sets context)
- Medial (middle): She, in the morning, jogs. (less common; used for stylistic effect)
- Final (end): She jogs in the morning. (most neutral and common)
4.3 Prepositions Commonly Used in Adverbial Phrases
| Function | Prepositions | Example Phrase |
|---|---|---|
| Time | at, in, on, during, after, before, until, since, by | after lunch |
| Place | under, over, between, among, near, at, on, beside, behind, inside | under the bridge |
| Manner | with, without, by, like, as | with care |
| Reason | because of, due to, owing to, thanks to | because of the rain |
| Condition | in case of, under | in case of emergency |
| Degree | to, by, at | to a great extent |
| Frequency | on, from, at | from time to time |
| Purpose | for, to | for safety |
4.4 Modifiers Inside the Phrase
Modifiers expand the noun/pronoun object, including:
- Articles: a, the
- Adjectives: cold, beautiful, large
- Determiners: my, his, their
- Compounds: winter morning, safety reasons
Example: during the long, hot summer
4.5 Step-by-Step Construction
Step 1: Choose a preposition based on the meaning.
e.g., after (time)
Step 2: Add the noun or pronoun object.
e.g., after lunch
Step 3: Expand with modifiers as needed.
e.g., after the important team lunch
Complete phrase: after the important team lunch
5. TYPES OR CATEGORIES OF ADVERB PREPOSITIONAL PHRASES
5.1 Time
Tell when an action happens.
- After the meeting
- During the night
- Before lunch
- At sunset
5.2 Place
Tell where something occurs.
- Under the bridge
- At the beach
- Near the school
- Between the buildings
5.3 Manner
Tell how something happens.
- With care
- Like a pro
- By hand
- Without hesitation
5.4 Reason or Cause
Explain why.
- Because of the rain
- Due to illness
- Owing to traffic
- Thanks to his efforts
5.5 Condition
Express circumstances.
- In case of emergency
- Under certain conditions
- In the event of failure
5.6 Degree or Measure
Describe extent.
- To a great extent
- By a large margin
- At full capacity
5.7 Frequency
Tell how often.
- On occasion
- From time to time
- At regular intervals
5.8 Purpose
Explain the intended goal.
- For better results
- For safety
- For your information
In the next section, we provide 100 categorized examples with sentences and notes.
6. EXAMPLES SECTION (100 Examples)
6.1 Organization & Conceptual Notes
The following tables categorize 100 adverb prepositional phrases into their main functions. Each phrase is used in a contextualized sentence with explanations.
6.2 Example Tables
| Phrase | Sentence | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| after the meeting | We will discuss the plan after the meeting. | When? After event |
| before dawn | Before dawn, the hikers started their journey. | Early time |
| during the night | The alarm sounded during the night. | While night lasted |
| at midnight | The fireworks began at midnight. | Exact time |
| by noon | Please finish the report by noon. | Deadline |
| since last week | I have been sick since last week. | Duration start |
| until next year | The store is closed until next year. | End point |
| in the morning | He practices yoga in the morning. | Part of day |
| on Monday | The meeting is scheduled on Monday. | Specific day |
| after dinner | They went for a walk after dinner. | Later in time |
| over the weekend | I relaxed over the weekend. | Time span |
| within an hour | They arrived within an hour. | Time limit |
| throughout the day | Rain fell throughout the day. | Continuous duration |
| during lunch | She called me during lunch. | Inside time period |
| at sunset | Birds return at sunset. | Specific time |
| Phrase | Sentence | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| at the beach | They spent the day at the beach. | Location |
| under the bridge | The boat passed under the bridge. | Below place |
| between the trees | A deer appeared between the trees. | Intermediate |
| near the station | Let’s meet near the station. | Close by |
| on the roof | A cat sat on the roof. | Surface |
| behind the house | The garden is behind the house. | Rear position |
| inside the building | The conference is held inside the building. | Interior |
| in the city | She lives in the city. | Area |
| at home | I work at home. | Location |
| along the river | They walked along the river. | Beside |
| across the street | The shop is across the street. | Opposite |
| among friends | He felt confident among friends. | Within group |
| outside the gate | The car is parked outside the gate. | Exterior |
| beside the lake | They had a picnic beside the lake. | Next to |
| over the hill | The town lies over the hill. | Beyond |
| Phrase | Sentence | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| with care | Handle the glass with care. | How? Carefully |
| like a pro | She played tennis like a pro. | As a professional |
| by hand | The craftsman made the bowl by hand. | Manually |
| without hesitation | He accepted the offer without hesitation. | Confidently |
| in silence | They observed the ceremony in silence. | Quietly |
| with enthusiasm | She participated with enthusiasm. | Energetically |
| in a hurry | They left in a hurry. | Quickly |
| like a child | He laughed like a child. | Comparison |
| with a smile | She greeted me with a smile. | Cheerfully |
| without warning | The storm hit without warning. | Suddenly |
| under pressure | He works well under pressure. | Stress condition |
| with confidence | She spoke with confidence. | Assertively |
| by mistake | I deleted the file by mistake. | Accidentally |
| like an expert | He fixed the car like an expert. | Skill comparison |
| with passion | The actor performed with passion. | Emotionally |
| Phrase | Sentence | Notes |
|---|---|---|
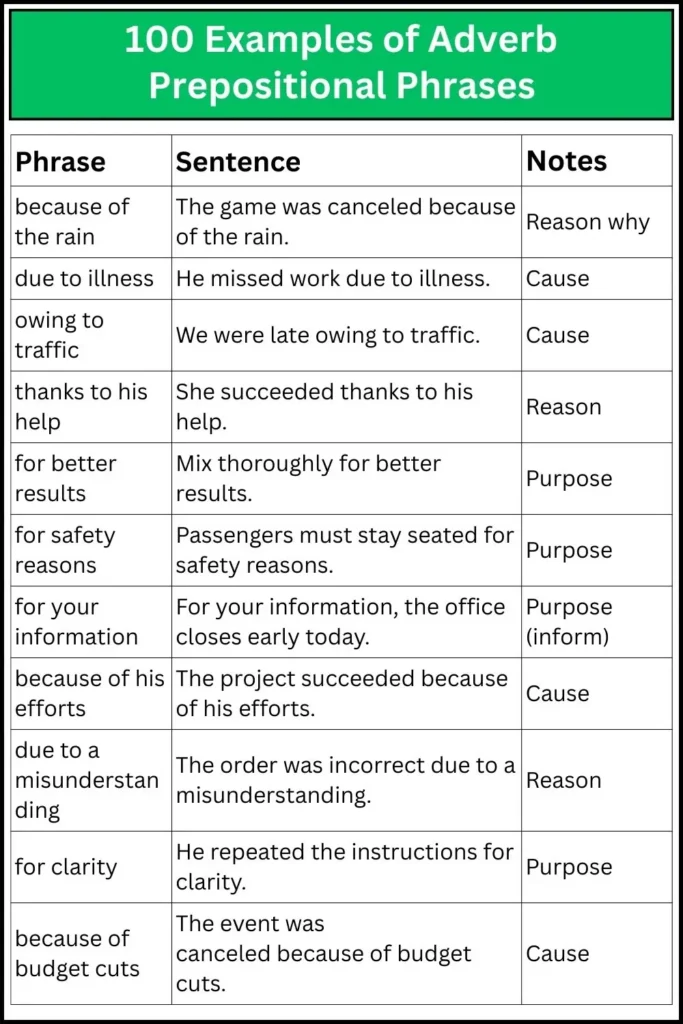
| because of the rain | The game was canceled because of the rain. | Reason why |
| due to illness | He missed work due to illness. | Cause |
| owing to traffic | We were late owing to traffic. | Cause |
| thanks to his help | She succeeded thanks to his help. | Reason |
| for better results | Mix thoroughly for better results. | Purpose |
| for safety reasons | Passengers must stay seated for safety reasons. | Purpose |
| for your information | For your information, the office closes early today. | Purpose (inform) |
| because of his efforts | The project succeeded because of his efforts. | Cause |
| due to a misunderstanding | The order was incorrect due to a misunderstanding. | Reason |
| for clarity | He repeated the instructions for clarity. | Purpose |
| because of budget cuts | The event was canceled because of budget cuts. | Cause |
| for future reference | Please save this email for future reference. | Purpose |
| due to unforeseen circumstances | The flight was delayed due to unforeseen circumstances. | Reason |
| because of technical issues | Service was interrupted because of technical issues. | Cause |
| for maintenance | The system is offline for maintenance. | Purpose |
| Phrase | Sentence | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| in case of emergency | In case of emergency, call 911. | Condition |
| under certain conditions | The warranty applies under certain conditions. | Condition |
| to a great extent | He improved to a great extent. | Degree |
| by a large margin | They won by a large margin. | Degree |
| at full capacity | The factory is operating at full capacity. | Degree |
| under review | The proposal is under review. | Condition/state |
| to some extent | I agree to some extent. | Degree |
| in the event of failure | In the event of failure, notify your supervisor. | Condition |
| at minimum cost | We aim to complete the project at minimum cost. | Degree/Goal |
| by no means | He is by no means inexperienced. | Extent (negative) |
| Phrase | Sentence | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| from time to time | I visit my hometown from time to time. | Occasionally |
| on occasion | He travels abroad on occasion. | Sometimes |
| at regular intervals | The bell rings at regular intervals. | Periodically |
| once in a while | We go hiking once in a while. | Sporadically |
| every now and then | I indulge every now and then. | Occasionally |
| on a daily basis | He exercises on a daily basis. | Daily frequency |
| at times | The task is challenging at times. | Sometimes |
| over the years | Her skills improved over the years. | Gradual frequency |
| on weekends | They relax on weekends. | Weekly |
| from week to week | The schedule changes from week to week. | Variable frequency |
6.3 Summary Notes
- Phrases often double as expressions of multiple functions, e.g., for safety reasons (purpose + reason).
- Some are idiomatic, e.g., by hand, on occasion.
- Register varies: due to unforeseen circumstances is more formal, while once in a while is informal.
- Regional preferences exist but most phrases are widely understood.
7. USAGE RULES
7.1 Correct Placement
Placing phrases at the beginning adds emphasis or sets context and usually requires a comma:
After the meeting, we went home.
Final position is neutral:
We went home after the meeting.
7.2 Agreement and Parallelism
Maintain parallel structure when listing:
Correct: She worked with diligence and with care.
Incorrect: She worked with diligence and carefully. (mixes phrase and adverb)
7.3 Choosing Prepositions
Be aware of subtle differences:
- in vs. on: in the morning (period), on Monday (day)
- with vs. by: with a hammer (instrument held), by train (means of transport)
7.4 Avoiding Ambiguity
Placement can change meaning or cause confusion:
She spoke to the man with a smile. (She smiled)
She spoke to the man with a smile. (Man has the smile)
7.5 Formal vs. Informal Contexts
Choose phrases appropriate for your audience:
- Due to unforeseen circumstances (formal)
- Because of a problem (neutral)
7.6 Special Cases & Exceptions
- Idioms: by heart, for good
- Phrases with implied parts: After lunch (is over)
- Some phrases fixed by usage: at night, not *in the night
8. COMMON MISTAKES
8.1 Misidentifying the Phrase’s Function
Confusing adjective and adverb phrases:
- The man with a smile greeted us. (adjective phrase, modifies “man”)
- She greeted us with a smile. (adverb phrase, modifies “greeted”)
8.2 Incorrect Preposition Choice
Incorrect: on the night
Correct: at night
8.3 Redundant Prepositions
Incorrect: inside of the house
Correct: inside the house
8.4 Misplaced Phrases Leading to Confusion
Incorrect: Walking through the park, the flowers bloomed beautifully. (Implies flowers were walking)
Correct: Walking through the park, I admired the blooming flowers.
8.5 Overuse or Wordiness
Overloaded: He went to the store with his friend in the afternoon on foot.
Better: He walked to the store with his friend in the afternoon.
8.6 Incorrect Examples and Corrections
| Incorrect | Correct | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| I will see you in Monday. | I will see you on Monday. | Use on for days. |
| She arrived on time with a hurry. | She arrived on time and in a hurry. | Parallel structure needed. |
| He went inside of the house. | He went inside the house. | Drop “of”. |
| The report is under the review. | The report is under review. | Omit “the”. |
| At night, she likes to walk on the park. | At night, she likes to walk in the park. | “In” for enclosed spaces. |
9. PRACTICE EXERCISES
9.1 Fill-in-the-Blank (Use the phrase bank)
Phrase Bank: at night, with care, because of the rain, under the bridge, before lunch, in silence, thanks to his help, on weekends, from time to time, for safety reasons
- They postponed the picnic __________.
- We meditate __________.
- The train passes __________.
- She studies __________.
- The package must be handled __________.
- They go hiking __________.
- The cat hides __________.
- He succeeded __________.
- They usually eat out __________.
- I like to take a short walk __________.
9.2 Identify the Function
Underline the prepositional phrase and label: Time, Place, Manner, Reason, Condition, Degree, Frequency, or Purpose.
- We will meet after the game.
- The kids played in the garden.
- He fixed the bike with ease.
- The event was canceled due to bad weather.
- In case of emergency, push the button.
- She improved to a large extent.
- I call my parents every now and then.
- He wore gloves for protection.
- They arrived before sunrise.
- The team won by a narrow margin.
9.3 Correction Exercise
Identify and correct mistakes.
- He will arrive in Monday.
- She spoke with loudly voice.
- The dog ran inside of the house.
- Because of of the accident, the road closed.
- They met on the park.
- In the night, the owl hunts.
- He sang with happiness and confidence.
- Owing traffic, we were late.
- The letter was sent by mistake accidentally.
- At weekends, she relaxes at home.
9.4 Sentence Construction
Write a sentence using each phrase.
- under review
- with passion
- over the years
- in a hurry
- due to illness
- on occasion
- for your information
- before dawn
- inside the building
- by a large margin
9.5 Matching Exercise
| Phrase | Category |
|---|---|
| because of the rain | |
| at midnight | |
| with a smile | |
| from time to time | |
| in case of emergency | |
| on the roof | |
| to a great extent | |
| for better results |
9.6 Answer Keys
Fill-in-the-Blank Answers:
- because of the rain
- in silence
- under the bridge
- at night
- with care
- from time to time
- before lunch
- thanks to his help
- on weekends
- for safety reasons
Identify Function Answers:
- Time
- Place
- Manner
- Reason
- Condition
- Degree
- Frequency
- Purpose
- Time
- Degree
Correction Exercise Answers:
- He will arrive on Monday.
- She spoke loudly or with a loud voice.
- The dog ran inside the house.
- Because of the accident, the road was closed.
- They met in the park.
- At night, the owl hunts.
- He sang with happiness and with confidence.
- Owing to traffic, we were late.
- The letter was sent by mistake.
- On weekends, she relaxes at home.
Matching Exercise Answers:
| Phrase | Category |
|---|---|
| because of the rain | Reason |
| at midnight | Time |
| with a smile | Manner |
| from time to time | Frequency |
| in case of emergency | Condition |
| on the roof | Place |
| to a great extent | Degree |
| for better results | Purpose |
10. ADVANCED TOPICS
10.1 Layering Multiple Adverb Prepositional Phrases
Multiple phrases add rich detail:
She arrived on time with a smile after a long journey.
10.2 Ellipsis and Reduced Phrases
Shortened for style:
After lunch (is over), we’ll meet.
10.3 Idiomatic Expressions with Prepositional Phrases
- by all means (certainly)
- in the blink of an eye (very quickly)
- at a loss (uncertain)
10.4 Prepositional Phrases in Passive Constructions
The cake was eaten in the morning.
10.5 Distinguishing Prepositional Phrases from Adverb Clauses
- Before the sun rose (clause—has subject + verb)
- Before sunrise (phrase—no verb)
10.6 Nuances in Formal vs. Informal Registers
- due to (formal)
- because of (neutral/informal)
11. FAQ SECTION
- What is an adverb prepositional phrase, and how is it different from an adjective prepositional phrase?
An adverb prepositional phrase modifies verbs, adjectives, or adverbs, answering questions like when, where, how. An adjective prepositional phrase modifies a noun or pronoun, answering which one? - Can a single prepositional phrase modify multiple elements in a sentence?
Sometimes, especially when modifying compound verbs or adjectives, but clarity is key; otherwise, use separate phrases. - Are there restrictions on where adverb prepositional phrases can be placed?
Generally flexible, but initial placement often adds emphasis and requires a comma. Avoid confusing placements in the middle of sentences. - What are the most common prepositions used in adverbial phrases?
At, in, on, by, with, after, before, because of, due to, under, over, near, during. - How can I tell if a prepositional phrase is essential or non-essential?
If removing it changes the core meaning, it’s essential. If it adds extra detail, it’s non-essential and often comma-separated. - What is the difference between because of and due to?
Because of modifies verbs and is more neutral. Due to traditionally modifies nouns and is more formal, though in casual speech they’re often interchangeable. - Can multiple adverb prepositional phrases be used in one sentence?
Yes! Layering adds detail, but avoid overloading sentences and ensure clarity. - Should I always use a comma after an introductory adverb prepositional phrase?
Use a comma when the phrase is long (4+ words) or for clarity/emphasis. Short phrases can omit it. - How do adverb prepositional phrases improve sentence variety?
They allow flexible sentence openings and add descriptive detail, making writing richer and more precise. - What are some common idiomatic adverb prepositional phrases?
By heart, in vain, at a glance, by all means, on purpose, at once. - Are there differences in usage between American and British English?
Minor; for example, at the weekend (BrE) vs. on the weekend (AmE). Most phrases are common to both. - How can I practice and master using these phrases correctly?
Read widely, notice usage, complete exercises like those here, write your own sentences, and seek feedback.
12. CONCLUSION
Adverb prepositional phrases are vital tools in English, enabling you to add nuance, clarity, and vivid detail to your communication. By understanding their structure, functions, and usage rules, you can craft more precise and engaging sentences.
This guide provided:
- Clear definitions and distinctions
- Structural breakdowns with examples
- 100 categorized, contextualized example phrases
- Usage rules and common mistake corrections
- Extensive practice exercises
- Advanced insights and FAQs
Keep practicing by incorporating these phrases into your speaking and writing. Review the examples and tables regularly. As you master adverb prepositional phrases, you’ll find your English becomes more fluent, expressive, and sophisticated.
Happy learning!

