Verbs are the backbone of every sentence, bringing action and meaning to communication. While some verbs can stand alone and complete a thought, others require additional elements to fully convey their meaning. These additional elements help paint a clearer picture of the action. Among these, complex transitive verbs are key players in creating more detailed and descriptive sentences.
In this article, we’ll explore General Complex Transitive Verbs Starting with BU. These verbs are not only diverse in meaning but also versatile in usage, making them invaluable tools in both written and spoken communication. We will dive into their definitions, provide examples, and show you how to effectively incorporate them into your daily vocabulary.
Whether you’re a student looking to improve your writing or someone aiming to refine your language skills, this guide will help you better understand complex transitive verbs and how they can enhance your sentence structure.
What Are Transitive Verbs?
In simple terms, transitive verbs are action verbs that require a direct object to complete their meaning. The direct object is the noun or pronoun that receives the action of the verb. Without this object, the sentence may feel incomplete or lack clarity.
For example, in the sentence “She reads the book,” the verb “reads” is transitive because it is acting on the direct object “the book”. If you say, “She reads,” the sentence feels unfinished and doesn’t convey a full thought.
Transitive verbs are divided into two main categories:
- Simple Transitive Verbs: These verbs only need a direct object to complete their meaning. For instance, in the sentence “He ate the cake,” “ate” is a simple transitive verb and “cake” is the direct object.
- Complex Transitive Verbs: These verbs require both a direct object and an additional complement to complete their meaning. The complement can be a noun, adjective, or phrase that adds more information. For example, in the sentence “She considers him a genius,” the verb “considers” is complex, and “him” is the direct object, while “a genius” acts as the complement, explaining what he is considered.
Complex transitive verbs add depth to your sentences and help express more detailed actions and relationships between subjects and objects.
General Complex Transitive Verbs Starting with BU.
1. Build
Definition:
To construct or form something by putting parts or materials together.
Example:
- The architect built the house with care.
Here, “with care” is the complement that describes how the action was carried out.
Why It’s Useful:
“Build” is a versatile verb that can be used in various contexts, from physical construction to metaphorical uses, such as building relationships or building confidence.
2. Burn
Definition:
To consume or damage something with fire or intense heat.
Example:
- The fire burned the house to the ground.
“To the ground” complements the object, showing the extent of the damage.
Why It’s Useful:
“Burn” can describe both literal and figurative actions. It helps convey intensity, whether talking about physical fire or emotional distress.
3. Bust
Definition:
To break, burst, or damage something, often resulting in destruction.
Example:
- The storm busted the windows wide open.
The complement “wide open” gives us further detail about the action.
Why It’s Useful:
“Bust” is a dynamic verb often used to describe sudden or forceful action. It adds energy and emphasis to sentences.
4. Buy
Definition:
To acquire something by paying for it.
Example:
- She bought him a gift for his birthday.
In this case, “for his birthday” is the complement, explaining the reason for the action.
Why It’s Useful:
“Buy” is an essential verb in everyday conversation. Understanding its use as a complex transitive verb can help clarify the purpose or intention behind the purchase.
5. Butter
Definition:
To spread or coat something with butter or a similar substance.
Example:
- She buttered the toast with extra butter.
Here, “with extra butter” tells us how the action was performed.
Why It’s Useful:
This verb is practical for describing a specific action in cooking or food preparation. It’s a simple way to convey attention to detail when preparing food.
6. Blur
Definition:
To make something unclear or indistinct, often by smearing or obscuring it.
Example:
- The rain blurred the windshield completely.
The complement “completely” adds more detail about the extent of the blurring.
Why It’s Useful:
“Blur” is an effective verb for describing actions that make things difficult to perceive. It’s useful in both literal and metaphorical contexts, such as vision or memories.
7. Buckle
Definition:
To fasten something with a buckle, often used with belts or straps.
Example:
- He buckle the seatbelt safely.
“Safely” tells us how the action is done, adding an important detail.
Why It’s Useful:
This verb is commonly used in everyday tasks related to safety and fastening. It’s an important verb in both literal and figurative senses.
8. Bungle
Definition:
To carry out a task clumsily or ineptly.
Example:
- He bungled the job completely.
Here, “completely” serves as a complement, emphasizing the extent of the failure.
Why It’s Useful:
“Bungle” helps convey a sense of failure or incompetence. It’s often used in professional or informal situations to explain mistakes or blunders.
9. Buck
Definition:
To resist or oppose something forcefully.
Example:
- The horse bucked the rider off.
The complement “off” shows where the rider was ejected.
Why It’s Useful:
“Buck” is often used to describe resistance, whether physical (as in animals) or metaphorical (such as bucking authority). It adds a sense of struggle or defiance to sentences.
10. Bustle
Definition:
To move energetically or with a lot of activity.
Example:
- She bustled around the house getting ready for the party.
The complement adds a layer of detail, showing what she was preparing for.
Why It’s Useful:
“Bustle” is useful when describing action-filled scenarios, particularly in busy environments. It adds motion and urgency to descriptions.
11. Butter
Definition:
To apply butter to something.
Example:
- She buttered the bread generously.
“Generously” serves as a complement describing how the action was done.
Why It’s Useful:
This verb is practical in cooking and food contexts, adding flavor to both language and meaning when discussing food preparation.
12. Build
Definition:
To create or construct something.
Example:
- They built the house with great care.
The complement “with great care” describes the manner in which the house was constructed.
Why It’s Useful:
“Build” is frequently used in both literal and figurative contexts, such as creating physical structures or building relationships and ideas.
13. Buzz
Definition:
To make a buzzing sound or cause something to make such a sound.
Example:
- The bee buzzed around the flowers constantly.
“Constantly” describes how the action was done.
Why It’s Useful:
“Buzz” adds a sense of liveliness or activity to descriptions, often evoking a sense of motion and sound in narrative.
14. Bum
Definition:
To ask for something, typically in an informal or casual manner.
Example:
- He bummed a ride from his friend.
“From his friend” clarifies the object of the action.
Why It’s Useful:
“Bum” is colloquial and useful for casual conversations, often when describing situations of needing help or favors.
15. Bulk
Definition:
To form a large mass or quantity of something.
Example:
- The workers bulk the materials into one pile.
Here, the complement “into one pile” specifies the result of the action.
Why It’s Useful:
“Bulk” is useful for conveying large quantities or actions that involve gathering and organizing, commonly used in business and logistics contexts.
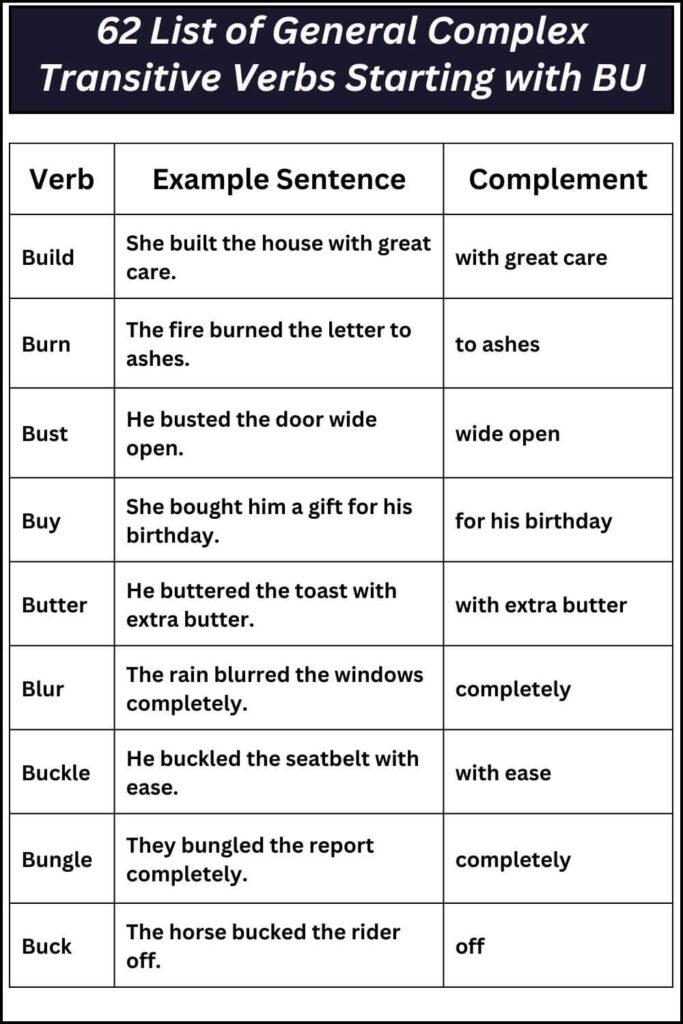
62 List of General Complex Transitive Verbs Starting with BU
Below is a comprehensive table of 62 complex transitive verbs that begin with the letters “BU”. These verbs can help expand your vocabulary and add more depth to your writing.
| Verb | Example Sentence | Complement |
|---|---|---|
| Build | She built the house with great care. | with great care |
| Burn | The fire burned the letter to ashes. | to ashes |
| Bust | He busted the door wide open. | wide open |
| Buy | She bought him a gift for his birthday. | for his birthday |
| Butter | He buttered the toast with extra butter. | with extra butter |
| Blur | The rain blurred the windows completely. | completely |
| Buckle | He buckled the seatbelt with ease. | with ease |
| Bungle | They bungled the report completely. | completely |
| Buck | The horse bucked the rider off. | off |
| Bustle | The workers bustled around the office. | around the office |
| Butter | She buttered the bread generously. | generously |
| Build | They built the project with diligence. | with diligence |
| Buzz | The bees buzzed around the flowers constantly. | constantly |
| Bum | He bummed a ride from his friend. | from his friend |
| Bulk | They bulked the material into large piles. | into large piles |
| Burnish | She burnished the brass until it gleamed. | until it gleamed |
| Buoy | The raft buoyed the passengers across the river. | across the river |
| Budget | They budgeted the funds efficiently for the event. | efficiently |
| Buffer | The cushion buffered the impact of the fall. | the impact |
| Burden | She burdened him with too many responsibilities. | with too many responsibilities |
| Buzz | The alarm buzzed in the morning. | in the morning |
| Bungle | He bungled the project due to poor planning. | due to poor planning |
| Buckle | She buckled the shoes tightly. | tightly |
| Bail | He bailed the car out of the muddy road. | out of the muddy road |
| Beat | She beat the eggs for the cake batter. | for the cake batter |
| Burst | The balloon burst with a loud pop. | with a loud pop |
| Buzz | His phone buzzed with notifications. | with notifications |
| Budge | The heavy box wouldn’t budge an inch. | an inch |
| Burnish | The students burnished their resumes for the job. | their resumes for the job |
| Bum | He bummed a dollar from his neighbor. | from his neighbor |
| Burp | The baby burped after feeding. | after feeding |
| Bluster | The politician blustered about his plans. | about his plans |
| Bulk | The cargo was bulked into containers. | into containers |
| Back | She backed the car into the driveway. | into the driveway |
| Bomb | The team bombed the competition badly. | the competition badly |
| Buffer | The extra room buffers the noise from outside. | the noise from outside |
| Buy | He bought the painting for a high price. | for a high price |
| Burrow | The rabbit burrowed the hole deeper. | the hole deeper |
| Buzz | The phone buzzed with a message. | with a message |
| Battle | They battled the opponent with strong strategy. | with strong strategy |
| Budge | The team budged their position slightly. | their position slightly |
| Buttle | He buttled up the jacket and wore it proudly. | up the jacket |
| Blush | She blushed the cheeks of the child. | the cheeks of the child |
| Bustle | The chefs bustled around the kitchen. | around the kitchen |
| Bundle | He bundled the clothes for donation. | the clothes for donation |
| Banish | The king banished the knight for treason. | the knight for treason |
| Burden | She burdened him with all the work. | with all the work |
| Build | The company built the app to enhance productivity. | the app to enhance productivity |
| Broach | He broached the idea at the meeting. | the idea at the meeting |
| Balance | She balanced the plates on her head carefully. | the plates on her head |
| Behead | The king beheaded the traitor in the square. | the traitor in the square |
| Bandage | He bandaged the wound swiftly. | the wound swiftly |
| Buff | He buffed the floors to a shine. | the floors to a shine |
| Blunt | The worker blunted the edge of the knife. | the edge of the knife |
| Button | She buttoned her coat in the chilly air. | her coat in the chilly air |
| Bloom | The flowers bloomed with vibrant colors. | with vibrant colors |
| Ban | He banned the books from the library. | the books from the library |
FAQs On General Complex Transitive Verbs Starting with BU
1. What is a complex transitive verb?
A complex transitive verb is a verb that requires both a direct object and an additional complement (such as an adjective, noun, or phrase) to complete the meaning. For example, in the sentence “She made him happy,” “made” is the complex transitive verb, “him” is the direct object, and “happy” is the complement.
2. Why are complex transitive verbs important?
They add richness and detail to sentences, helping to convey more specific meanings. They allow for more precise expression, especially when describing actions and their effects.
3. Can you give more examples of complex transitive verbs?
Yes, examples include verbs like “build,” “burn,” “buckle,” and “buy,” as seen throughout the article.
4. How do I use complex transitive verbs in everyday writing?
Incorporating complex transitive verbs can make your writing more engaging. Whether in storytelling, business communication, or casual conversations, these verbs help convey clearer and more detailed ideas.
Conclusion On Complex transitive verbs that start with BU
Understanding complex transitive verbs that start with BU enhances your vocabulary and ability to express yourself more clearly and accurately. These verbs provide additional nuance and detail in both written and spoken communication. By recognizing their structure and usage, you can elevate your language skills and make your sentences more dynamic.
Incorporating verbs like build, buy, and burn with their appropriate complements will give your sentences clarity, depth, and more descriptive power. Keep practicing, and these verbs will soon become an essential part of your everyday vocabulary.

