Noun suffixes are one of the most important building blocks of English grammar. They allow us to transform words, adding richness and variety to the language. Understanding noun suffixes not only helps in expanding vocabulary but also improves writing and speaking skills.
In this article, we’ll explore what noun suffixes are, how they function, and provide you with a detailed list of 50 common noun suffixes. We’ll also give examples to help you see how they work in context.
What Are Noun Suffixes?
A noun suffix is a letter or group of letters added to the end of a base word (root word) to form a noun. The suffix changes the word’s meaning, and often, its grammatical function. These suffixes can indicate various aspects of the noun, such as its origin, role, or the quality it describes.
For example:
- -ness (happiness): Converts an adjective into a noun, indicating a state or quality.
- -er (worker): Turns a verb into a noun, indicating a person performing an action.
Why Are Noun Suffixes Important?
- Vocabulary Expansion: Adding suffixes to base words helps us create new words and expand our vocabulary.
- Grammatical Function: Noun suffixes help in identifying the role of the word in a sentence.
- Meaning Enhancement: They provide additional meaning and context to words, making communication more precise.
- Word Formation: Noun suffixes help form words that express concepts, ideas, or objects.
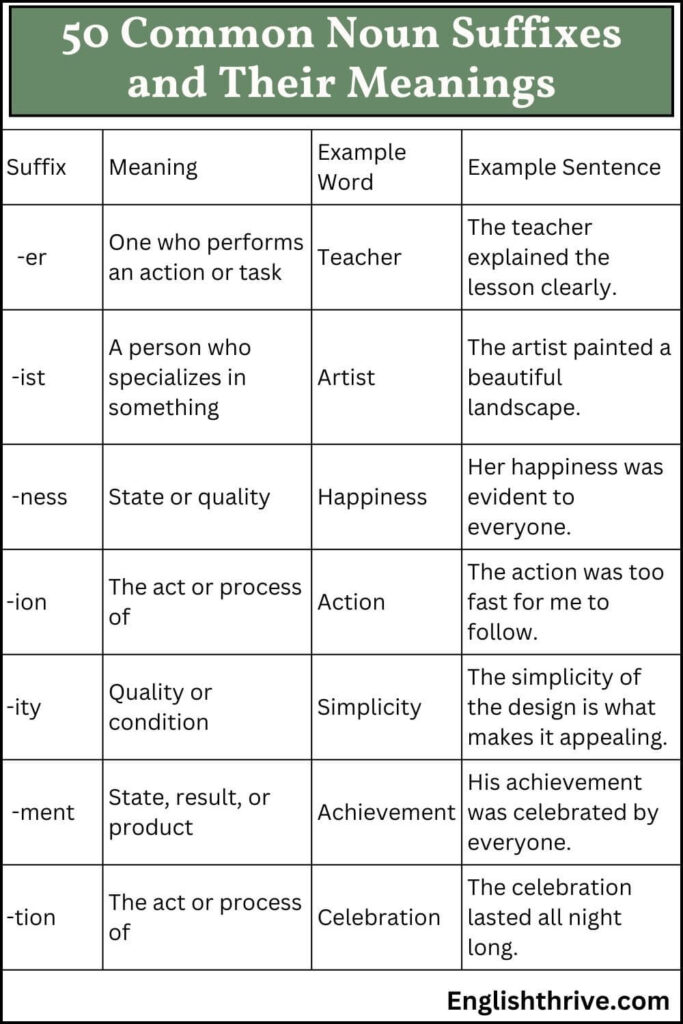
50 Common Noun Suffixes and Their Meanings
Here is a list of 50 noun suffixes, along with their meanings and examples to help you understand how each suffix is used in context:
| Suffix | Meaning | Example Word | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|---|
| -er | One who performs an action or task | Teacher | The teacher explained the lesson clearly. |
| -ist | A person who specializes in something | Artist | The artist painted a beautiful landscape. |
| -ness | State or quality | Happiness | Her happiness was evident to everyone. |
| -ion | The act or process of | Action | The action was too fast for me to follow. |
| -ity | Quality or condition | Simplicity | The simplicity of the design is what makes it appealing. |
| -ment | State, result, or product | Achievement | His achievement was celebrated by everyone. |
| -tion | The act or process of | Celebration | The celebration lasted all night long. |
| -hood | State, condition, or quality | Childhood | His childhood memories were full of adventure. |
| -dom | State, condition, or realm | Freedom | The country fought for its freedom. |
| -ance | Action, process, or state | Tolerance | Her tolerance for others is inspiring. |
| -ence | Action, process, or state | Silence | The silence in the room was deafening. |
| -ship | State, condition, or quality | Friendship | Their friendship lasted for decades. |
| -age | Related to a specific group or collection | Village | The village was small but charming. |
| -al | Pertaining to or related to | Criminal | The criminal was arrested for theft. |
| -ary | Relating to, connected with | Secretary | The secretary scheduled all the meetings. |
| -cy | State, condition, or quality | Accuracy | His accuracy in measurements was impressive. |
| -ology | The study of | Biology | She majored in biology at university. |
| -ism | A belief, practice, or philosophy | Realism | His painting style is characterized by realism. |
| -ify | To make or become | Magnify | The lens will magnify the small print. |
| -er | Comparative (often denotes the more) | Larger | The larger building overshadowed the smaller one. |
| -ess | Female or feminine role | Actress | The actress received an award for her performance. |
| -or | One who performs an action | Doctor | The doctor prescribed medicine for the illness. |
| -ee | One who receives or is affected by an action | Employee | The employee worked overtime to finish the task. |
| -ity | Quality, state | Creativity | Her creativity knows no bounds. |
| -ism | Practice, belief, or philosophy | Idealism | His idealism was evident in all his work. |
| -ment | Result or product of an action | Development | The development of the project took months. |
| -ness | State or condition | Darkness | The darkness of the night was overwhelming. |
| -y | Characterized by, inclined to | Honesty | Her honesty made her a trusted friend. |
| -ship | Group, condition, or profession | Leadership | He showed excellent leadership during the project. |
| -dom | State, condition, or realm | Kingdom | The kingdom was ruled by a wise king. |
| -hood | State or quality | Adulthood | Adulthood brings new responsibilities. |
| -age | Action, collection, or related to a place | Marriage | The couple celebrated their 25th wedding anniversary. |
| -y | Characterized by, or filled with | Beauty | The beauty of the landscape took my breath away. |
| -er | One who performs an action | Singer | The singer performed at the concert last night. |
| -ment | Process or action | Improvement | His improvement was visible after a few months of practice. |
| -ory | Related to or serving as | Category | This is the appropriate category for your submission. |
| -ance | Action, process, or state | Assistance | She offered her assistance with the project. |
| -ence | Action or process | Experience | Her experience with the team made her an excellent leader. |
| -hood | Condition or state | Brotherhood | Brotherhood is about supporting one another. |
| -dom | State, condition, or realm | Wisdom | His wisdom is sought by many. |
| -ity | Quality or state | Sensitivity | Sensitivity to others’ feelings is essential. |
| -ory | Place or function | Laboratory | The laboratory is where experiments are conducted. |
| -ment | Action or result | Enjoyment | We had a lot of enjoyment at the picnic. |
How to Use Noun Suffixes Effectively in Sentences
Now that we’ve discussed the definition and provided a list of common noun suffixes, it’s time to explore how to effectively use them in sentences. Understanding how noun suffixes change the meaning of words is important, but knowing how to use them properly in your writing will make your sentences more precise and varied.
Let’s look at how you can incorporate noun suffixes into your sentences and use them to express different nuances of meaning.
Using Noun Suffixes to Create Nouns from Adjectives
Many noun suffixes transform adjectives into nouns. This is especially useful when you want to talk about a state, condition, or quality.
Examples:
- -ness (Happiness, Sadness, Darkness)
- The happiness on her face was undeniable.
- He couldn’t escape the sadness that followed the bad news.
- -ity (Simplicity, Purity, Activity)
- The simplicity of the design made it easy to understand.
- Purity is often seen as a desirable quality in a person.
How It Works:
These noun suffixes help express a concept or condition (e.g., happiness, simplicity). This is useful when you want to describe abstract qualities or states rather than concrete objects.
Using Noun Suffixes to Form Agent Nouns
Agent nouns are nouns that refer to a person or thing that performs an action. Suffixes like -er, -or, and -ist are commonly used to form these nouns.
Examples:
- -er (Teacher, Worker, Player)
- The teacher gave us an interesting lesson today.
- He’s a hardworking worker who is always on time.
- -ist (Artist, Pianist, Scientist)
- She’s a talented artist with a unique style.
- The scientist made a breakthrough discovery in the lab.
How It Works:
These suffixes transform verbs into nouns, helping you talk about a person or object that performs the action. For example, a “worker” is someone who works, and an “artist” is someone who creates art.
Using Noun Suffixes to Indicate a State or Condition
Certain noun suffixes are used to show a state, condition, or quality of being. These nouns often describe situations or abstract concepts.
Examples:
-ship (Friendship, Partnership, Leadership)
- Their friendship lasted for many years.
- He showed excellent leadership skills during the meeting.
-hood (Childhood, Adulthood, Brotherhood)
- Childhood is often considered the most carefree time of life.
- They shared a strong sense of brotherhood during their time in the army.
How It Works:
These noun suffixes describe a state or a period in life, often referring to stages of personal growth, relationships, or societal roles.
Creating Abstract Nouns with Suffixes
Some noun suffixes are particularly useful for creating abstract nouns that refer to concepts or ideas rather than physical things. These nouns often describe intangible qualities or states of being.
Examples:
-ance (Importance, Tolerance, Elegance)
- The importance of being on time cannot be overstated.
- Her elegance was evident in the way she carried herself.
-tion (Celebration, Communication, Action)
- There was a great celebration after the victory.
- Clear communication is key to successful teamwork.
How It Works:
These suffixes help you create nouns that represent non-physical things, like qualities, actions, or ideas. This is especially helpful when you need to express complex thoughts or concepts.
Using Noun Suffixes to Express a Group or Collection
Some noun suffixes help to describe a collection or a group of things. These can refer to physical groups or more abstract collections.
Examples:
-ery (Bakery, Gallery, Brewery)
- The bakery sells fresh bread every morning.
- They visited an art gallery to admire modern paintings.
-age (Marriage, Village, Package)
- Their marriage was celebrated with a grand ceremony.
- The village is famous for its traditional festivals.
How It Works:
Suffixes like -ery and -age create nouns that refer to a collection of items, a place where specific activities happen, or even the result of a particular action.
Noun Suffixes in Professional Terminology
In professional and academic contexts, noun suffixes are often used to describe roles, processes, or areas of study.
Examples:
-ology (Biology, Psychology, Sociology)
- He studied psychology to understand human behavior.
- Sociology examines the behavior of groups and societies.
-ism (Realism, Feminism, Nationalism)
- Realism in art captures scenes from everyday life.
- Her passion for feminism led her to advocate for equal rights.
How It Works:
These suffixes are often used to describe fields of study or belief systems. They are essential for academic writing and discussions related to various disciplines.
Practical Tips for Mastering Noun Suffixes
As we conclude our exploration of noun suffixes, let’s focus on some practical tips that can help you better understand and use them in your daily writing and speaking. By integrating these strategies, you’ll enhance your vocabulary and strengthen your grasp of the English language.
1. Identify the Suffix’s Function
The first step in mastering noun suffixes is understanding what function each suffix serves. Are you transforming an adjective into a noun? Are you talking about a person, place, thing, or abstract concept? Identifying the role of the suffix will help you choose the right word for your needs.
Example:
- -ness: Changes an adjective into a noun to describe a state or quality (e.g., “happiness”).
- -er: Refers to a person who does something (e.g., “teacher”).
By categorizing suffixes, you can easily apply them to your writing and improve your understanding of their purpose.
2. Practice with Lists and Flashcards
One effective way to get comfortable with noun suffixes is to create lists of words that use the same suffix. This method allows you to see how different root words combine with suffixes. You can also make flashcards, with the root word on one side and the noun form on the other.
Example:
- -ness: happiness, sadness, kindness, darkness
- -er: teacher, runner, player, singer
This repetition helps reinforce the connection between the root word and its new meaning.
3. Use Suffixes in Context
The best way to learn noun suffixes is to use them in context. Start by identifying words in articles, books, or conversations that use these suffixes. Then, try to incorporate these words into your own sentences. This will help solidify your understanding and usage of the suffixes.
Example:
- Read a sentence like, “The teacher encouraged us to be kind to others.”
- Then write your own sentence: “Her kindness made everyone smile.”
This practice will also help you expand your vocabulary naturally.
4. Pay Attention to Word Families
Many words share common suffixes and are part of word families. For example, the suffix -ly (which forms adverbs) often pairs with adjectives to create related nouns and adjectives. Understanding word families will help you see the connections between words and suffixes.
Example:
- Happy (adjective) → Happiness (noun)
- Care (verb) → Carefulness (noun)
Focusing on word families gives you the ability to better navigate the different forms of words and how they relate to one another.
5. Start Writing with Noun Suffixes
As you build your vocabulary with noun suffixes, start incorporating them into your writing exercises. Whether it’s a journal entry, essay, or short story, the more you write, the more you’ll gain confidence using noun suffixes. Try writing in different contexts, such as describing people, places, or abstract concepts, to practice diverse uses.
Final Thoughts on Mastering Noun Suffixes
Noun suffixes are incredibly useful tools for expanding your vocabulary and enhancing your writing. By understanding the different types of noun suffixes, their meanings, and how they transform words, you can significantly improve your ability to express complex ideas and concepts. Remember to practice regularly, read widely, and keep experimenting with new words.
The more you engage with noun suffixes in everyday writing and conversation, the more fluent and confident you’ll become in using them. So, keep practicing, and watch your language skills grow!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Noun Prefixes and Suffixes
What are the prefixes and suffixes of nouns?
Prefixes and suffixes are affixes that modify the meaning of the base word. While prefixes appear at the beginning of a word, suffixes are added to the end. For nouns, prefixes generally alter the meaning of the noun (often changing its state or indicating the opposite), while suffixes often indicate the word’s grammatical category or provide additional meaning.
- Examples of noun prefixes: un- (unhappiness), re- (recovery), dis- (disability)
- Examples of noun suffixes: -ness (happiness), -ment (achievement), -er (teacher)
What is noun suffixes with examples?
A noun suffix is a group of letters added to the end of a word to form a noun. These suffixes often help identify the role of the word in a sentence or give it a particular meaning. Common noun suffixes include -ness, -ment, -er, and -ion.
- Examples:
- -ness: happiness, sadness, darkness
- -ment: enjoyment, movement, treatment
- -er: teacher, runner, player
- -ion: action, decision, creation
What is a noun prefix example?
A noun prefix is a set of letters added to the beginning of a base word to modify its meaning. Prefixes can change the noun’s meaning to express negation, position, time, or other aspects.
- Examples:
- un-: unhappy (negation)
- pre-: prehistory (time-related)
- dis-: disagreement (opposite or removal)
- re-: return (again)
- anti-: antibiotic (against)
What is the suffix for a noun?
A suffix for a noun is a group of letters added at the end of a base word to create a noun. These suffixes often change the part of speech and add meaning related to quality, state, or profession.
- Common noun suffixes include:
- -ness: happiness, darkness
- -ment: enjoyment, achievement
- -er: teacher, driver
- -ion: nation, action
- -ity: activity, diversity
Meta Description: Master noun suffixes in English with 50 common suffixes and practical tips. Learn how to use them effectively and expand your vocabulary for better writing and communication.

