Verbs are the backbone of any sentence, and in English, understanding the different forms and patterns they follow is crucial for effective communication. One group of verbs that you may come across frequently are verbs that end with ss. These verbs, though not as numerous as others, play an essential role in everyday language and are a critical component of fluent and accurate English.
Whether you’re a student learning English, a writer refining your grammar, or a professional enhancing your communication skills, understanding verbs that end with ss will greatly improve your command of the language. This guide will cover everything you need to know about these verbs, from their definitions and examples to how they are used in sentences.
What Are Verbs That End With Ss?
Verbs that end with ss are verbs in their base form that end with the letters “ss.” These verbs are typically regular, following standard conjugation rules. Most of these verbs are simple to conjugate in the present tense, where you add -es for the third-person singular subject (he, she, it).
For example:
- Pass becomes passes in the present tense when referring to third-person singular subjects.
- Kiss becomes kisses in the present tense for third-person singular subjects.
Key Features of Verbs That End With Ss:
- These verbs end with -ss in their base form.
- They are generally regular verbs and follow standard conjugation patterns.
- -ss verbs are frequently used in everyday conversations and written English.
Common Words That End With Ss
In this section, we’ll explore some of the most commonly used verbs that end with ss. These verbs are often encountered in various contexts, from casual conversations to professional communication.
List of Common Verbs Ending with Ss:
- Pass
- Kiss
- Miss
- Class
- Guess
- Dress
- Stress
- Press
- Reassess
- Express
Each of these verbs serves a unique function in a sentence, and knowing how to use them properly will significantly enhance your language skills.
Example Sentences:
- Pass: He passes the ball to his teammate.
- Kiss: She kisses her mother goodbye every morning.
- Miss: I miss the train this morning.
- Class: The teacher class will begin at 10 AM.
- Guess: Can you guess who I met yesterday?
- Dress: She dresses very stylishly for work.
- Stress: It’s important not to stress about small things.
- Press: Please press the button to start the machine.
- Reassess: After reviewing the report, they decided to reassess the situation.
- Express: I express my gratitude for your help.
60 Verbs That End With Ss
| Verb | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Pass | She passes the test with ease. |
| Kiss | They kissed at the airport. |
| Miss | He misses his family every holiday. |
| Class | The students class in their books. |
| Guess | I guess she will be late to the party. |
| Dress | She dresses in the latest fashion. |
| Stress | He stressed the importance of time management. |
| Press | He presses the button to start the machine. |
| Reassess | They will reassess their decision next week. |
| Express | She expresses her feelings through art. |
| Address | He addresses the crowd with confidence. |
| Access | She accesses the website regularly. |
| Confess | He confesses his mistakes openly. |
| Impress | She impresses everyone with her performance. |
| Distress | The storm distressed the community. |
| Suppress | The coach suppressed his frustration after the game. |
| Process | He processes the data efficiently. |
| Compress | They compress the files for storage. |
| Redress | They redressed the grievance in the meeting. |
| Repress | He repressed his emotions after the accident. |
| Access | He accesses his email multiple times a day. |
| Success | She successfully managed the event. |
| Assess | The manager assesses the situation carefully. |
| Express | They expressed their opinions clearly. |
| Progress | We progress towards the goal each day. |
| Compress | He compresses the files before sending them. |
| Possess | She possesses great leadership skills. |
| Obsess | He obsesses over every little detail. |
| Repress | She repressed her anger during the meeting. |
| Success | She celebrates every small success. |
| Access | The team accesses the database frequently. |
| Address | The president addresses the nation tonight. |
| Confess | The witness confessed his involvement. |
| Impress | She impresses everyone with her knowledge. |
| Reassess | The company will reassess the project timelines. |
| Suppress | He tried to suppress his excitement. |
| Process | We need to process the information quickly. |
| Compress | They compress the files to save space. |
| Distress | The news distressed her greatly. |
| Address | She addressed the crowd with clarity. |
| Confess | He confessed his feelings for her. |
| Press | Please press the button to start. |
| Dress | She dresses for success every day. |
| Impress | They were impressed by his speech. |
| Guess | I guess I will see you tomorrow. |
| Stress | She stressed the need for proper planning. |
| Success | The team’s success was well-deserved. |
| Reassess | We need to reassess our strategy for next year. |
| Express | She expressed concern about the issue. |
| Process | The system processes orders quickly. |
| Pass | They passed the exam with flying colors. |
| Kiss | He kissed her gently on the cheek. |
| Miss | I miss my hometown sometimes. |
| Class | The students class in the lecture hall. |
| Guess | I guess we can start the meeting. |
| Dress | She dresses for the event every year. |
| Stress | The situation stressed him out. |
| Press | She presses the remote to change the channel. |
| Reassess | We should reassess the project outcomes. |
| Address | The issue was addressed during the meeting. |
How to Use Verbs That End With Ss Correctly
Understanding how to use verbs that end with ss correctly is essential for fluency in both spoken and written English. These verbs are mostly regular, but there are some important rules to follow for proper conjugation and sentence structure. Let’s break down how to apply them correctly in various contexts.
Conjugating Verbs That End With Ss
The general rule for verbs that end with ss follows regular conjugation patterns in English. However, their usage can vary slightly based on tense, subject-verb agreement, and sentence structure.
Present Tense
When used in the present tense with third-person singular subjects (he, she, it), you typically add -es to the base form of the verb:
- Pass → He passes the ball to his teammate.
- Kiss → She kisses her mom every morning.
Past Tense
For the past tense, regular verbs ending in -ss simply add -ed:
- Miss → She missed the bus this morning.
- Dress → He dressed for the occasion yesterday.
Past Participle and Present Perfect
In the present perfect tense, you use the past participle form of the verb, which for most verbs that end with ss will also be -ed. The auxiliary verb has/have is used.
- Pass → He has passed the test.
- Kiss → She has kissed him on the cheek.
Negative Sentences
For negative sentences in the past tense, the auxiliary verb did not (or didn’t) is used, and the main verb returns to its base form (without the -ed ending):
- Pass → He did not pass the test.
- Kiss → She did not kiss him.
How Words That End With Ss Are Used in Sentences
Verbs that end with ss are used in many ways to describe actions in the past, habitual activities, or outcomes of actions. Let’s take a look at how they function in sentences.
Describing Actions in the Past
These verbs are most commonly used in the past tense to describe actions that have already occurred.
- Example: He passed the exam with flying colors.
Describing Repeated or Regular Actions
Some of these verbs are used to describe actions that are repeated or habitual.
- Example: She kisses her kids goodnight every evening.
Describing Events or Changes
These verbs can describe an event or a change that happened in the past.
- Example: They missed the concert because they were stuck in traffic.
Describing Emotional States or Reactions
Verbs like stress, impress, and express can describe emotional reactions or states in relation to people or events.
- Example: The announcement stressed the importance of safety measures.
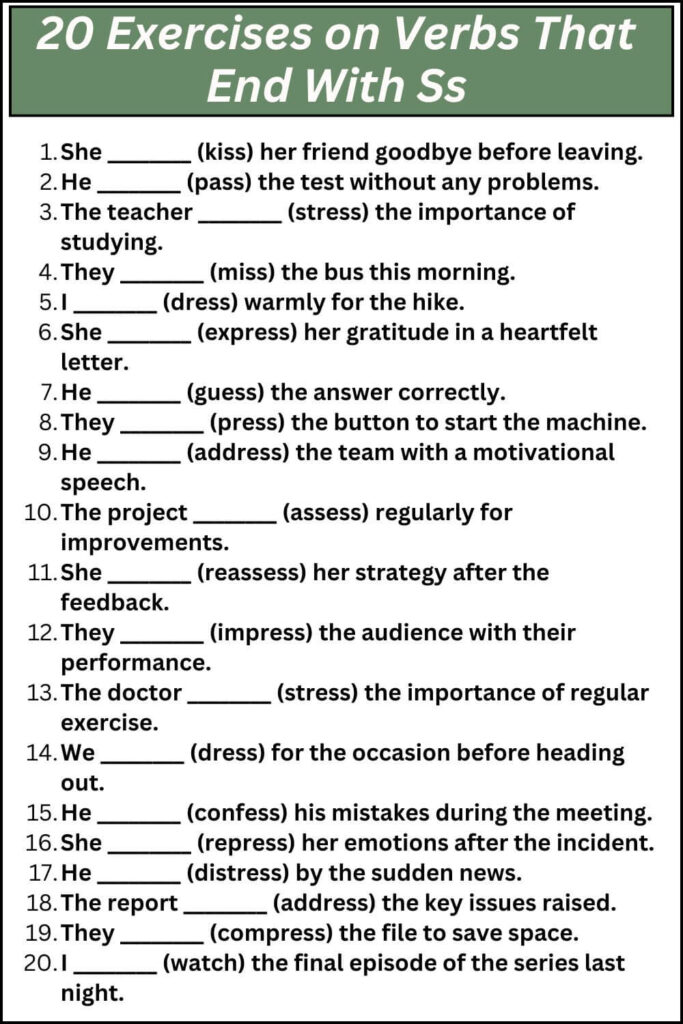
20 Exercises on Verbs That End With Ss
- She ________ (kiss) her friend goodbye before leaving.
- He ________ (pass) the test without any problems.
- The teacher ________ (stress) the importance of studying.
- They ________ (miss) the bus this morning.
- I ________ (dress) warmly for the hike.
- She ________ (express) her gratitude in a heartfelt letter.
- He ________ (guess) the answer correctly.
- They ________ (press) the button to start the machine.
- He ________ (address) the team with a motivational speech.
- The project ________ (assess) regularly for improvements.
- She ________ (reassess) her strategy after the feedback.
- They ________ (impress) the audience with their performance.
- The doctor ________ (stress) the importance of regular exercise.
- We ________ (dress) for the occasion before heading out.
- He ________ (confess) his mistakes during the meeting.
- She ________ (repress) her emotions after the incident.
- He ________ (distress) by the sudden news.
- The report ________ (address) the key issues raised.
- They ________ (compress) the file to save space.
- I ________ (watch) the final episode of the series last night.
Conclusion on Verbs That End With Ss
In conclusion, verbs that end with ss are essential components of the English language. They are commonly used in both casual and formal contexts to describe actions that have already occurred or to express habits, emotions, or changes. Mastering the use of these verbs will enhance your ability to communicate effectively, whether you are speaking, writing, or reading.
Final Tips for Mastery:
- Regularly practice conjugating verbs that end with ss to become more familiar with their forms.
- Pay attention to subject-verb agreement, especially when using third-person singular subjects.
- Incorporate these verbs into your daily conversations or writing to improve fluency and comfort.
By practicing these verbs and understanding their correct usage, you’ll enhance your ability to communicate clearly and confidently in English.