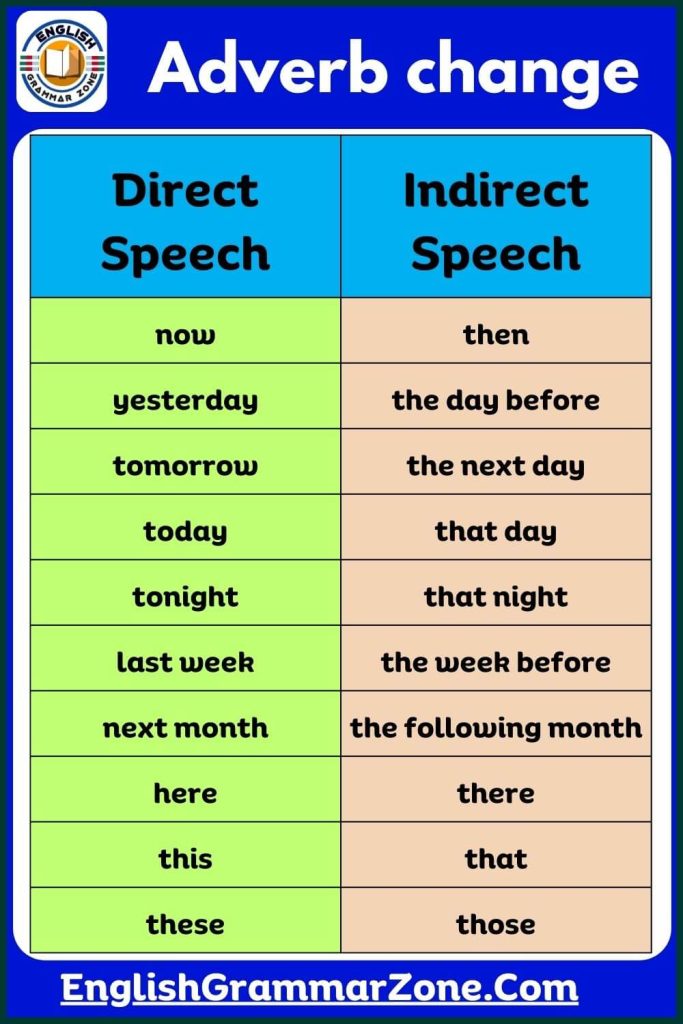
Adverb Change Chart With Examples
Adverb Change Chart provides a clear and simple guide to understanding how adverbs transform in different contexts, such as tense, speech, and sentence forms.
Direct and Indirect Speech
Definition of Speech:
- The communication or expression of thoughts in spoken words.
- Something that is spoken.
In spoken English, speech can be categorized into two types:
- Direct Speech
- Indirect Speech
These forms are used to convey a person’s spoken words to another person.
What is Direct & Indirect Speech?
Direct Speech: The speaker’s message is conveyed using their exact words without any changes. Example: Radha said, “I am very busy now.”
Note:
- The speaker’s exact words are enclosed in quotation marks.
- A comma or colon follows “said” to introduce the spoken words.
Indirect Speech: The speaker’s message is conveyed in our own words. Example: Radha said that she was very busy then.
Note:
- The word ‘that’ is used before the reported speech.
- Pronouns and other sentence elements are adjusted accordingly.
Components of Direct Speech: Direct Speech consists of two components:
- Reporting Speech: The part of the sentence before the actual words of the speaker (e.g., she said, he said). Examples:
- She said, “I am listening to music.”
- He says, “You are an intelligent student.”
- You will say, “I need your help.”
- Reported Speech: The speaker’s actual words enclosed in quotation marks. Examples:
- He said, “I got a job in college.”
- She says, “I want to become a doctor.”
- They said, “We play football in the playground.”
Rules for Changing Direct Speech to Indirect Speech:
- If the Reporting Verb is in Present or Future Tense: The tense of the verb in the Indirect Speech remains unchanged. Example: Balu says, “I eat a mango.” (D.S.) Balu says that he eats a mango. (I.S.)
- If the Reporting Verb is in Past Tense: The tense of the verbs in the Reported Speech must generally change.
- Present Tense becomes Past Tense. Example: Somu said, “I ask a doubt.” (D.S.) Somu said that he asked a doubt. (I.S.)
- Past Tense becomes Past Perfect or remains unchanged. Example: Arun said, “I ate a mango yesterday.” (D.S.) Arun said that he had eaten a mango the day before. (I.S.)
- Present Continuous becomes Past Continuous. Example: Charan said, “I am going to school.” (D.S.) Charan said that he was going to school. (I.S.)
- Past Continuous becomes Past Perfect Continuous. Example: Naveen said, “I was playing Ludo.” (D.S.) Naveen said that he had been playing Ludo. (I.S.)
- Present Perfect becomes Past Perfect. Example: Surya said, “I have done my homework.” (D.S.) Surya said that he had done his homework. (I.S.)
- Present Perfect Continuous becomes Past Perfect Continuous. Example: He said, “I have been studying English.” (D.S.) He said that he had been studying English. (I.S.)
- ‘Will’ and ‘Shall’ are changed to ‘would’. Example: He said, “I will do work tomorrow.” (D.S.) He said that he would do work the next day. (I.S.)
- Modal Verbs: ‘May’ becomes ‘might’, ‘can’ becomes ‘could’, ‘must’ becomes ‘had to/must’.
Exception: Universal truths remain unchanged in tense. Example: The teacher said, “The sun rises in the East.” (D.S.) The teacher said that the sun rises in the East. (I.S.)
Types of Sentences in Reported Speech:
Assertive Sentences:
- Remove quotation marks.
- Use the conjunction ‘that’.
- Change ‘say to’ into ‘tell’ and ‘said to’ into ‘told’. Examples:
- “I will work hard to get first class,” said Ramu. (D.S.) Ramu said that he would work hard to get first class. (I.S.)
- “You can do this work,” said Ram to Rani. (D.S.) Ram told Rani that she could do that work. (I.S.)
Imperative Sentences (Order/Request):
- Use ‘to’ for affirmative sentences and ‘not to’ for negative sentences.
- Omit ‘please’ and use ‘request’ instead of ‘say’.
- Change ‘say’ or ‘said’ to tell, request, order, command, etc. Examples:
- “Be careful,” he said to her. (D.S.) He ordered her to be careful. (I.S.)
- “Bring me a glass of water,” said the mother to her son. (D.S.) The mother asked her son to bring her a glass of water. (I.S.)
Interrogative Sentences (Questions):
- Remove quotation marks and the question mark.
- Use ‘if’ or ‘whether’ for yes/no questions.
- Use the given interrogative word for wh-questions.
- Change ‘say’ or ‘said’ to ‘ask’ or ‘enquire’. Examples:
- “Won’t you help me to carry this box?” I said to my friend. (D.S.) I asked my friend if he would help me carry that box. (I.S.)
- Mohan said to Sita, “Why didn’t you attend the meeting yesterday?” (D.S.) Mohan asked Sita why she hadn’t attended the meeting the day before. (I.S.)
Exclamatory Sentences:
- Change to a statement.
- Remove quotation marks and exclamatory marks.
- Use the conjunction ‘that’.
- Omit interjections like oh, alas, hurrah.
- Add ‘very’ to the adjective or adverb if necessary.
- Use ‘exclaim joyfully’ or ‘exclaim sorrowfully’. Examples:
- “Oh, what a beautiful flower that is!” she said. (D.S.) She exclaimed joyfully that it was a very beautiful flower. (I.S.)
- “What a horrible sight!” we all exclaimed. (D.S.) We all exclaimed that it was a very horrible sight. (I.S.)
Direct Speech Examples
- She said, “I am going to the market.”
- John said, “I will meet you at the park.”
- Mary said, “I have finished my homework.”
- He said, “I can swim very well.”
- They said, “We are planning a trip.”
- The teacher said, “Please open your books.”
- She said, “I love reading novels.”
- He said, “I need to buy groceries.”
- Jane said, “I visited my grandparents last weekend.”
- Tom said, “I will help you with your project.”
- They said, “We are watching a movie tonight.”
- She said, “I am feeling better now.”
- He said, “I will call you later.”
- The manager said, “We need to complete this task by tomorrow.”
- She said, “I am learning French.”
- He said, “I have been to Paris.”
- They said, “We enjoy playing football.”
- She said, “I want to become a doctor.”
- He said, “I am working on a new project.”
- The coach said, “You must practice every day.”
- She said, “I am cooking dinner.”
- He said, “I will arrive at 6 PM.”
- They said, “We are leaving for vacation next week.”
- She said, “I have lost my keys.”
- He said, “I am reading a fascinating book.”
- She said that she was going to the market.
- John said that he would meet me at the park.
- Mary said that she had finished her homework.
- He said that he could swim very well.
- They said that they were planning a trip.
- The teacher asked us to open our books.
- She said that she loved reading novels.
- He said that he needed to buy groceries.
- Jane said that she had visited her grandparents last weekend.
- Tom said that he would help me with my project.
- They said that they were watching a movie that night.
- She said that she was feeling better now.
- He said that he would call me later.
- The manager said that we needed to complete the task by the next day.
- She said that she was learning French.
- He said that he had been to Paris.
- They said that they enjoyed playing football.
- She said that she wanted to become a doctor.
- He said that he was working on a new project.
- The coach said that we must practice every day.
- She said that she was cooking dinner.
- He said that he would arrive at 6 PM.
- They said that they were leaving for vacation the following week.
- She said that she had lost her keys.
- He said that he was reading a fascinating book.
Adverb change rules